UML (Unified Modeling Language) Class Diagrams are a fundamental part of object-oriented system design. They provide a static structure view of a system by illustrating classes, their attributes, operations (methods), and the relationships between objects. This guide covers the essentials of UML Class Diagrams, drawing from standard practices to help you understand and create effective diagrams.
What is a UML Class Diagram?
A UML Class Diagram is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing:
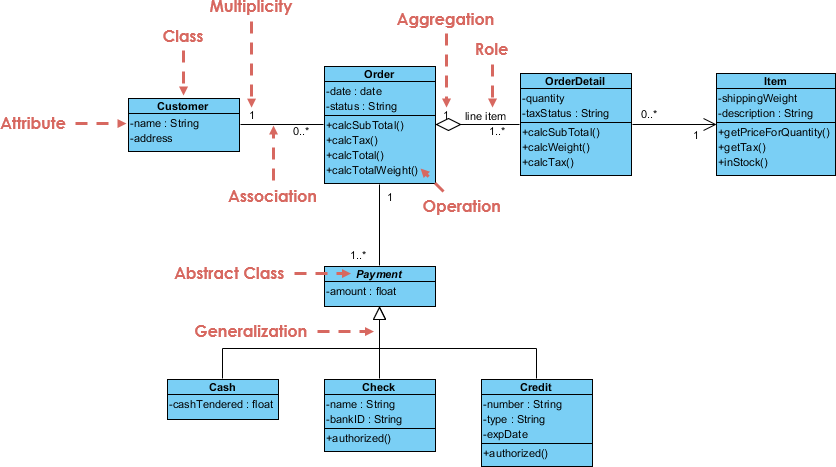
- Classes: The building blocks of the system.
- Attributes: Properties or data members of classes.
- Operations (Methods): Behaviors or functions provided by classes.
- Relationships: Connections among classes, such as inheritance, associations, and dependencies.
Class diagrams are essential for visualizing the blueprint of object-oriented systems, aiding in design, communication, and implementation.
What is a Class?
A class is a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that objects instantiated from the class will have.
- Objects are instances of classes.
- Example: A “Dog” class might define states like color, name, and breed, and behaviors like barking or eating. Each actual dog (e.g., “Fido”) is an object—an instance of the “Dog” class.
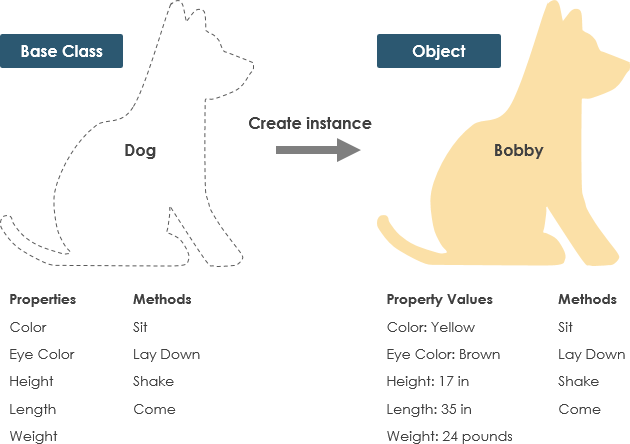
The focus of object-oriented design is on classes, as they enable the creation of reusable objects with shared components.
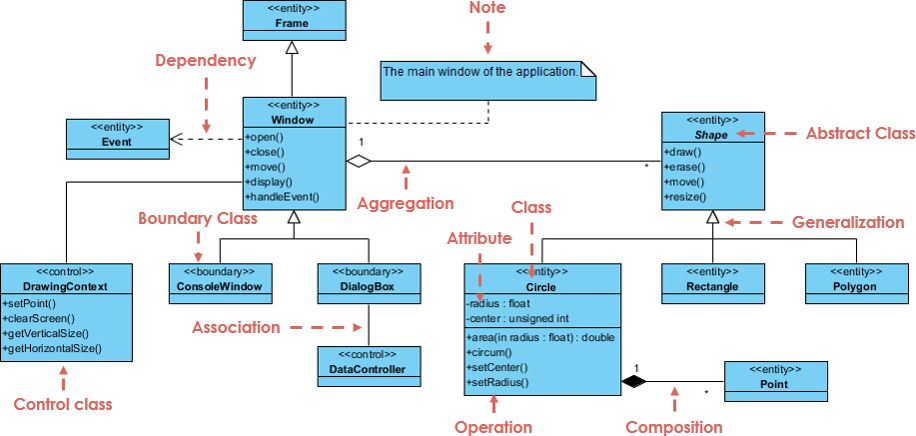
UML Class Notation
A class is represented as a rectangle divided into three compartments:
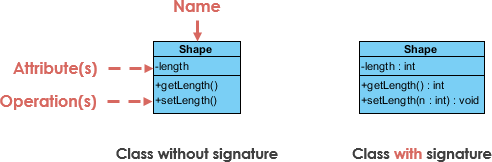
- Class Name (top compartment):
- The name of the class (mandatory).
- Abstract classes are shown in italics.
- Attributes (middle compartment):
- Listed as: visibility name : type
- Example: – name : String (private attribute).
- Operations (Methods) (bottom compartment):
- Listed as: visibility name(parameter : type) : returnType
- Example: + bark() : void (public method).
Visibility Indicators
- + : Public (accessible from anywhere)
- – : Private (accessible only within the class)
- # : Protected (accessible within the class and subclasses)
Parameter Directionality
Parameters in operations can include direction:
- in: Input parameter
- out: Output parameter
- inout: Both input and output
Perspectives of Class Diagrams
Class diagrams can be viewed from different perspectives depending on the development stage:
- Conceptual: Focuses on domain concepts (high-level, real-world entities).
- Specification: Emphasizes interfaces and abstract data types (ADTs) in software.
- Implementation: Details how classes implement interfaces (code-level).
The level of detail increases from conceptual to implementation.
Relationships Between Classes
Relationships define how classes interact. Common types include:
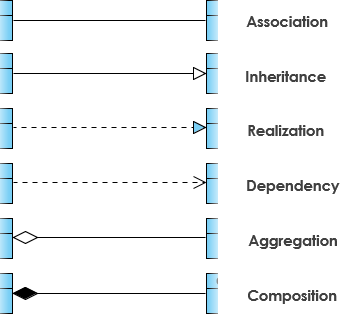
- Inheritance (Generalization):
- “Is-a” relationship.
- Represented by a solid line with a hollow arrowhead pointing to the parent class.
- Example: SubClass inherits from SuperClass.
- Association:
- Structural link between classes (e.g., “has-a”).
- Solid line.
- Can include cardinality (e.g., one-to-one, one-to-many *).
- Named with a verb phrase.
- Aggregation:
- “Part-of” relationship where parts have independent lifetimes.
- Solid line with an unfilled diamond at the whole end.
- Composition:
- Stronger aggregation where parts are destroyed with the whole.
- Solid line with a filled diamond at the whole end.
- Dependency:
- One class uses another temporarily (changes in one may affect the other).
- Dashed line with an open arrow.
- Realization:
- Implements an interface.
- Dashed line with a hollow arrowhead.
Class Diagram Examples
Order System Example
A typical order system might include:
- Classes: Customer, Order, OrderItem, Product, Payment.
- Relationships: Customer places Order (association), Order contains OrderItems (composition), OrderItem references Product (association).
GUI Example
For a graphical user interface:
- Classes: Window, Button, Panel, Label.
- Relationships: Window contains Panels and Buttons (composition), Button inherits from Component (inheritance).
Notes can be attached to classes or relationships for additional clarification.
Why Use Tools for Creating Class Diagrams?
Manual drawing can be time-consuming, especially for complex systems. Modern tools like Visual Paradigm accelerate the process with intuitive editors and support for all UML elements.
Recommendation: Visual Paradigm’s New AI-Powered Class Diagram Generation
Visual Paradigm offers powerful AI features to generate class diagrams quickly from text descriptions, making it ideal for both beginners and professionals.
Key benefits include:
- Rapid Prototyping and Efficiency:
- Transform a simple text prompt (e.g., “An online shopping system with users, products, carts, and orders”) into a complete, professionally laid-out class diagram in seconds.
- Saves hours on initial setup, allowing you to focus on refinement rather than manual drawing.
- Fully Editable Diagrams:
- Generated diagrams open directly in Visual Paradigm’s intuitive editor for easy modifications, additions, or adjustments.
- Unlike many AI tools that produce static images, these are live, refinable models.
- Proper Model Concepts and Consistency:
- AI generates diagrams with accurate UML elements: classes, attributes, operations, relationships (e.g., associations, inheritance, composition), and multiplicities.
- Ensures reusable, non-duplicated classes by intelligently identifying domain entities and avoiding redundancies (e.g., merging similar class names based on context).
- Includes best-practice checks, design critiques, and suggestions for maintainability.
- Avoids Limitations of Generic AI-Generated Diagrams:
- Many AI tools (e.g., general chatbots) produce one-off, non-editable images or code that can’t be refined easily.
- Visual Paradigm’s AI creates functional, editable models that integrate into your project workflow.
- Iterative and Refinable:
- Start with AI generation, then iteratively refine: add details, fix issues, or expand using guided steps, textual analysis, or further AI assistance (e.g., notes, reports).
- Supports export to PlantUML, SVG, or full project integration.
Visual Paradigm Community Edition is free for non-commercial use and supports core UML diagramming. For advanced AI features, explore their professional tools.
Download Visual Paradigm and try the AI-powered generation today to create high-quality class diagrams faster and more effectively!