Introduction
In the fast-paced world of software development, defining clear and comprehensive system requirements is a critical yet challenging task. Traditional methods of identifying use cases and manually drafting descriptions and diagrams are not only time-consuming but also prone to inconsistencies and errors.
Enter the Use Case Description Generator, an AI-powered tool designed to automate and standardize the use case modeling process.
This article explores the tool’s features, benefits, and practical applications, providing examples, key concepts, and a summary of its transformative impact on system analysis and design.
The Challenge of Defining Clear System Requirements
Common Pain Points
- Time-Consuming Process: Manually identifying use cases and drafting detailed descriptions can take hours or even days, delaying project timelines.
- Inconsistencies: Different analysts may interpret requirements differently, leading to inconsistent documentation.
- Human Error: Manual creation of use case diagrams can introduce errors, miscommunication, and incomplete requirements.
- Stakeholder Misalignment: Poorly documented use cases can result in software that fails to meet user needs.
Why Automation is Essential
Automating the use case modeling process ensures:
- Comprehensive Coverage: AI can identify potential use cases that might be overlooked manually.
- Consistency: Standardized descriptions and diagrams improve clarity and reduce ambiguity.
- Efficiency: Faster generation of use case models accelerates the transition from concept to design.
Introducing the Use Case Description Generator
What is the Use Case Description Generator?
The Use Case Description Generator is an AI-driven tool that transforms a simple problem statement into a detailed use case model. It automates the following steps:
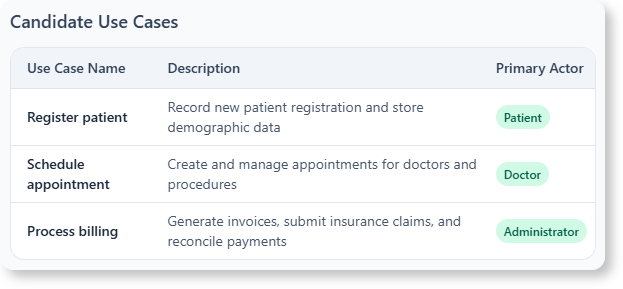
- Candidate Use Case Generation: Suggests relevant use cases based on the problem description.
- Detailed Use Case Description: Generates structured descriptions, including actors, pre-conditions, post-conditions, main flow, and alternative flows.
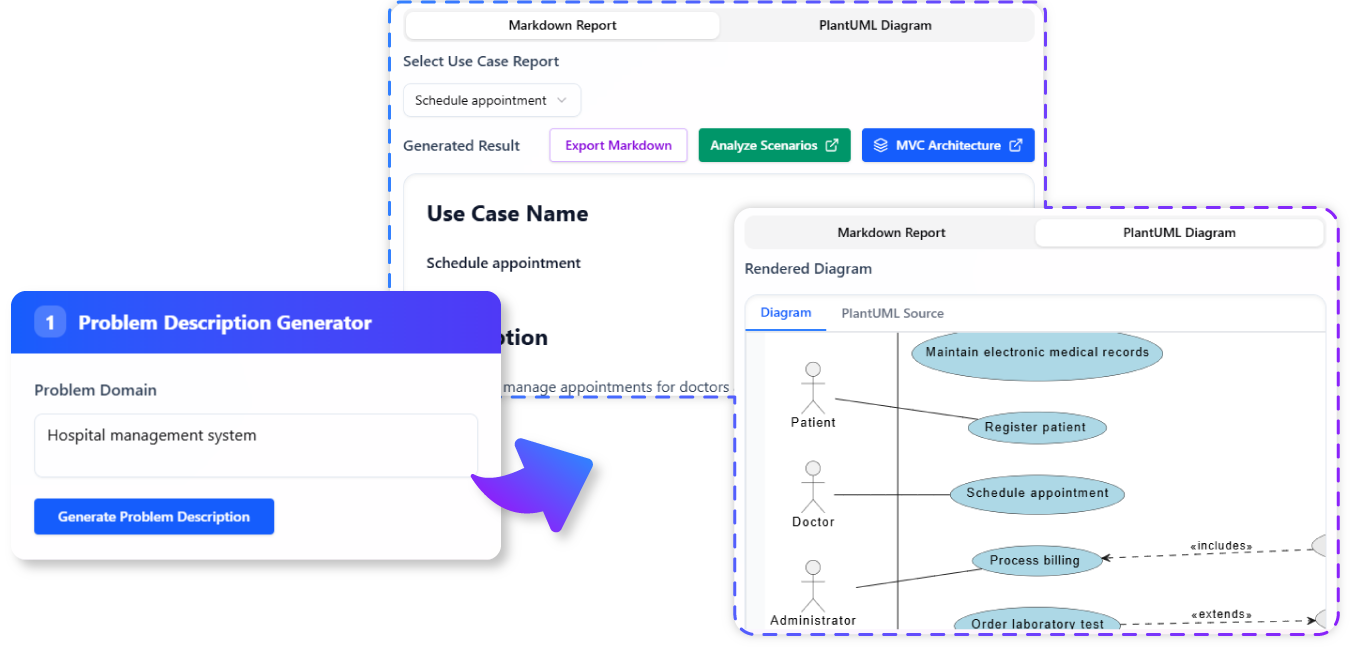
- PlantUML Diagram Generation: Creates visual representations of use cases for better understanding.
Key Features
- : Input a problem description, and the AI suggests a list of potential use cases.
- Detailed Use Case Descriptions: Automatically generates comprehensive descriptions for each use case.
- Instant PlantUML Diagrams: Provides visual diagrams to complement textual descriptions.
- Improved Clarity and Consistency: Standardizes documentation for all stakeholders.
- Accelerated System Analysis: Reduces the time and effort required to create detailed use case models.
How to Use the Use Case Description Generator
Step-by-Step Workflow
-
Input Problem Description:
- Provide a clear description of the problem your system aims to solve.
- Example: “A university wants to develop an online course registration system for students and faculty.”
-
Generate Candidate Use Cases:
- The AI analyzes the input and suggests potential use cases.
- Example Use Cases:
- Register for a Course
- Drop a Course
- View Course Catalog
- Manage Faculty Course Assignments
-
Select and Generate Detailed Description:
- Choose a use case, and the AI generates a structured description.
- Example for “Register for a Course”:
- Actors: Student, Course Registration System
- Pre-Conditions: Student must be logged in.
- Main Flow:
- Student selects a course from the catalog.
- System checks for prerequisites and availability.
- Student confirms registration.
- System updates the student’s course schedule.
- Post-Conditions: Student is enrolled in the selected course.
-
View PlantUML Diagram:
- The tool generates a visual diagram representing the use case.
- The tool generates a visual diagram representing the use case.
-
:
- Review and adjust the generated content.
- Export the use case model for further analysis or documentation.
Practical Examples
Example 1: Online Banking System
- Problem Description: “Develop an online banking system that allows customers to manage their accounts, transfer funds, and pay bills.”
- Candidate Use Cases:
- Log In to Account
- View Account Balance
- Transfer Funds
- Pay Bills
- Set Up Recurring Payments
- *Detailed Description for “Transfer Funds”:
- Actors: Customer, Banking System
- Pre-Conditions: Customer must be logged in and have sufficient funds.
- Main Flow:
- Customer selects “Transfer Funds.”
- System prompts for recipient details and amount.
- Customer confirms the transfer.
- System processes the transfer and updates both accounts.
- Post-Conditions: Funds are transferred, and both accounts reflect the change.
Example 2: Hospital Management System
- Problem Description: “Create a system for hospitals to manage patient records, appointments, and billing.”
- Candidate Use Cases:
- Schedule Appointment
- View Patient Records
- Generate Bill
- Update Patient Information
- *Detailed Description for “Schedule Appointment”:
- Actors: Receptionist, Patient, Hospital System
- Pre-Conditions: Patient must be registered in the system.
- Main Flow:
- Receptionist selects “Schedule Appointment.”
- System displays available time slots.
- Receptionist books an appointment for the patient.
- System sends a confirmation to the patient.
- Post-Conditions: Appointment is scheduled, and the patient receives confirmation.
Key Concepts and Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Use Case | A description of how a user interacts with a system to achieve a goal. |
| Actor | A user or external system that interacts with the system. |
| Pre-Condition | A condition that must be true before a use case can begin. |
| Post-Condition | A condition that must be true after a use case completes. |
| Main Flow | The primary sequence of steps in a use case. |
| Alternative Flow | A secondary sequence of steps that occurs if the main flow cannot proceed. |
| PlantUML | A language for creating UML diagrams using plain text. |
Benefits of Using the Use Case Description Generator
For Developers and Analysts
- Saves Time: Automates the generation of use cases, descriptions, and diagrams.
- Reduces Errors: Minimizes human error in documentation and diagram creation.
- Enhances Collaboration: Provides a standardized format for all stakeholders.
For Stakeholders
- Clear Communication: Ensures everyone understands system requirements.
- Faster Decision-Making: Accelerates the design and approval process.
- Improved Quality: Results in software that better meets user needs.
Summary
The Use Case Description Generator is a game-changer for system analysis and design. By automating the creation of use case descriptions and diagrams, it eliminates manual effort, reduces inconsistencies, and accelerates the development process. Whether you’re designing an online banking system, a hospital management system, or any other software application, this tool provides the clarity and efficiency needed to bring your vision to life.
Ready to Streamline Your System Analysis?
- Visual Paradigm Online Users: Access the tool here.
- Visual Paradigm Desktop Users: Navigate to Tools > App > Use Case Description Generator.