1. Introduction
Background
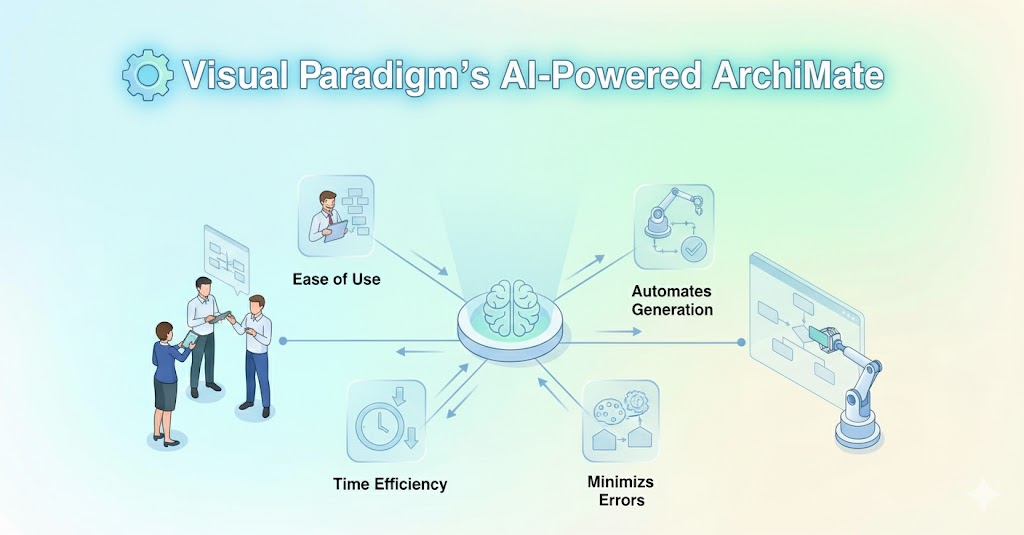
Object-Oriented Design (OOD) is a cornerstone of modern software engineering, but translating textual problem descriptions into structured UML Class Diagrams is often a manual, error-prone, and time-consuming process. Visual Paradigm’s AI Textual Analysis Tool aims to bridge this gap by automating and guiding the transformation of natural language into precise, visual class diagrams.
Objective
This case study explores how the AI Textual Analysis Tool streamlines the design process, reduces human error, and accelerates software development by leveraging AI-driven textual analysis.
2. Key Concepts
A. UML Class Diagrams
- Definition: A visual representation of classes, their attributes, methods, and relationships in an object-oriented system.
- Purpose: Serves as a blueprint for software architecture, ensuring clarity and consistency in design.
B. Textual Analysis in Software Design
- Definition: The process of extracting meaningful entities (classes, attributes, methods, relationships) from natural language descriptions.
- Challenges:
- Ambiguity in language.
- Overlooking critical entities or relationships.
- Time-consuming manual analysis.
C. AI-Powered Textual Analysis
- Definition: Using AI to automate the identification of classes, attributes, methods, and relationships from textual descriptions.
- Advantages:
- Reduces human bias and oversight.
- Accelerates the design phase.
- Ensures consistency and completeness.
3. The AI Textual Analysis Tool: Features and Workflow
A. Guided 6-Step Process
The tool follows a structured workflow to ensure thorough analysis:
| Step | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Problem Domain | Provide a high-level context of the system. | “A library management system for tracking books, members, and loans.” |
| 2. Problem Description | Enter a detailed description of the problem. | “The system should allow members to borrow books, track due dates, and send reminders.” |
| 3. Candidate Classes | Identify potential classes from the description. | Book, Member, Loan, Notification |
| 4. Class Details | Define attributes and methods for each class. | Book: title (String), author (String), isAvailable (Boolean); borrowBook() |
| 5. Relationships | Establish associations between classes. | Member → Loan (1-to-many), Book → Loan (1-to-many) |
| 6. Class Diagram | Generate a UML Class Diagram. | Visual output with classes, attributes, methods, and relationships. |
B. AI Assistance
- Entity Identification: The AI suggests potential classes, attributes, and methods based on the problem description.
- Relationship Mapping: The tool helps define associations, aggregations, and compositions between classes.
- Validation: Ensures no critical elements are overlooked.
4. Practical Example: Library Management System
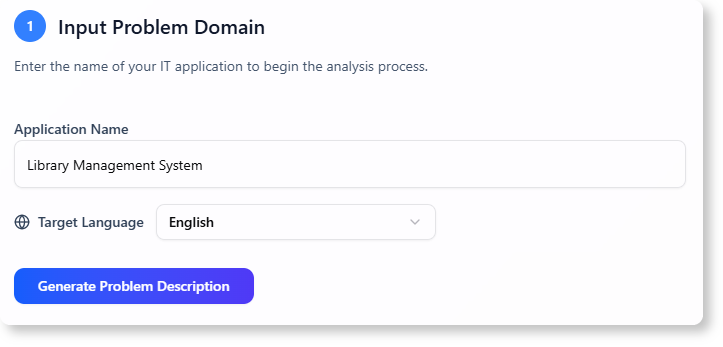
A. Problem Domain
“A digital library system for managing books, members, and loans.”
B. Problem Description
“The system should allow members to borrow and return books. It should track due dates, send reminders for overdue books, and manage member accounts. Librarians should be able to add or remove books and members.”
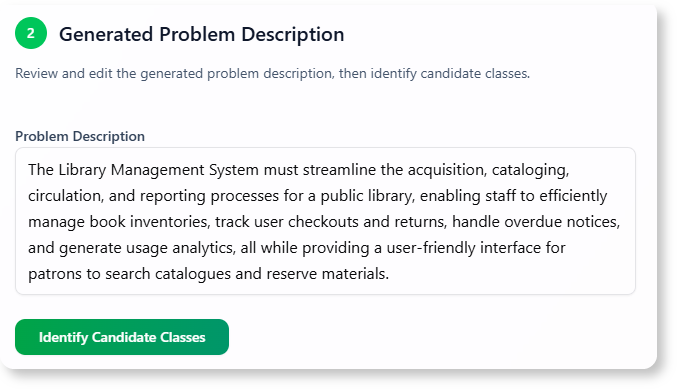
C. Candidate Classes
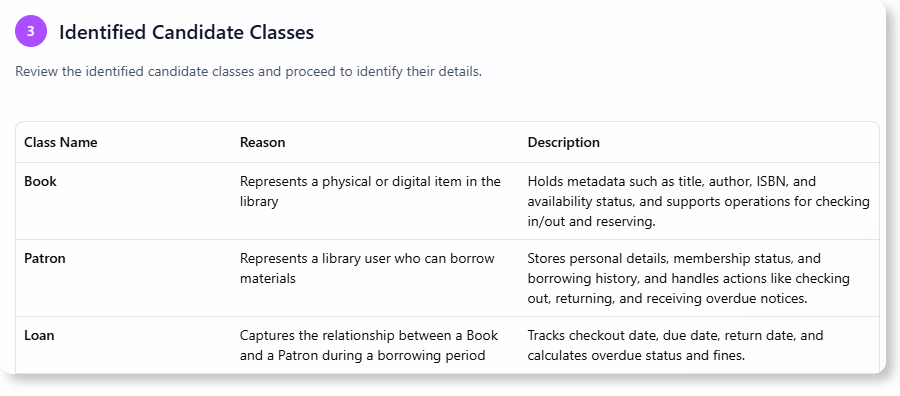
- Book
- Member
- Loan
- Notification
- Librarian
D. Class Details
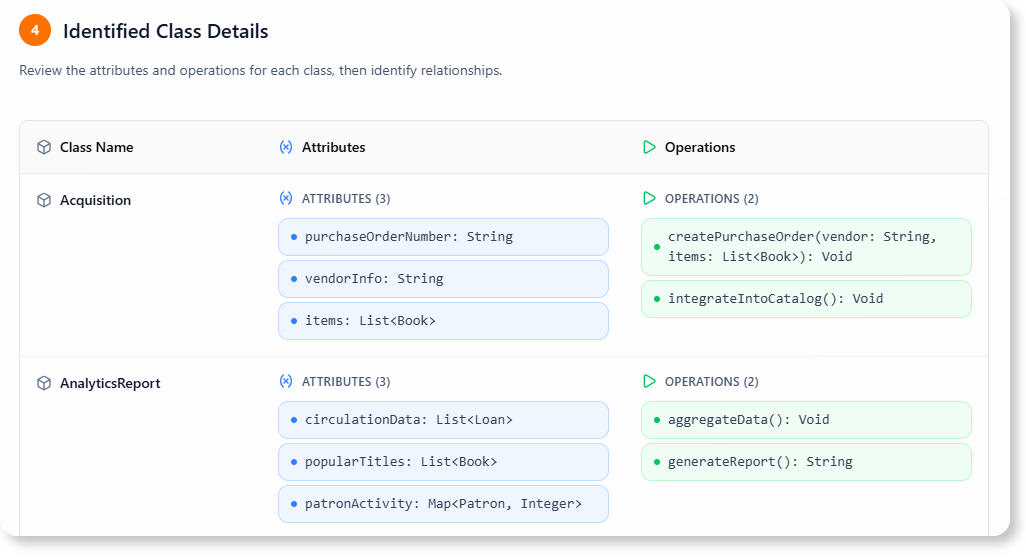
| Class | Attributes | Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Book | title (String), author (String), ISBN (String), isAvailable (Boolean) | borrowBook(), returnBook() |
| Member | name (String), memberID (String), email (String) | borrowBook(), returnBook() |
| Loan | loanID (String), dueDate (Date), isOverdue (Boolean) | calculateFine(), sendReminder() |
| Notification | message (String), dateSent (Date) | sendNotification() |
| Librarian | name (String), staffID (String) | addBook(), removeBook(), addMember() |
E. Relationships
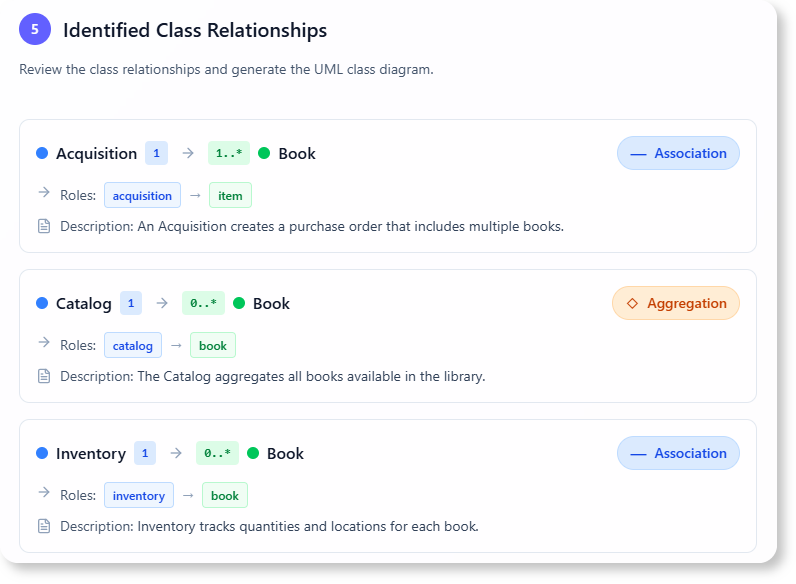
- Member → Loan (1-to-many)
- Book → Loan (1-to-many)
- Loan → Notification (1-to-1)
- Librarian → Book (1-to-many)
- Librarian → Member (1-to-many)
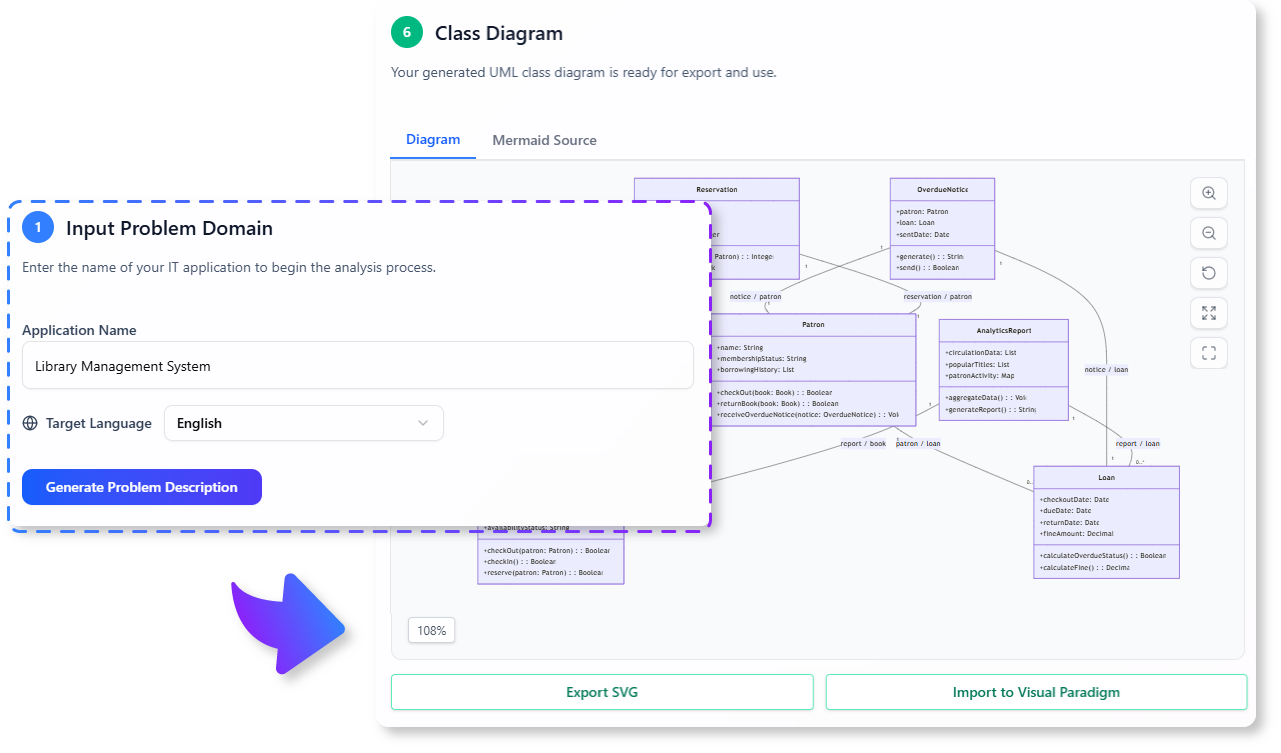
F. Generated UML Class Diagram
The tool generates a visual diagram with all classes, attributes, methods, and relationships, providing a clear blueprint for developers.
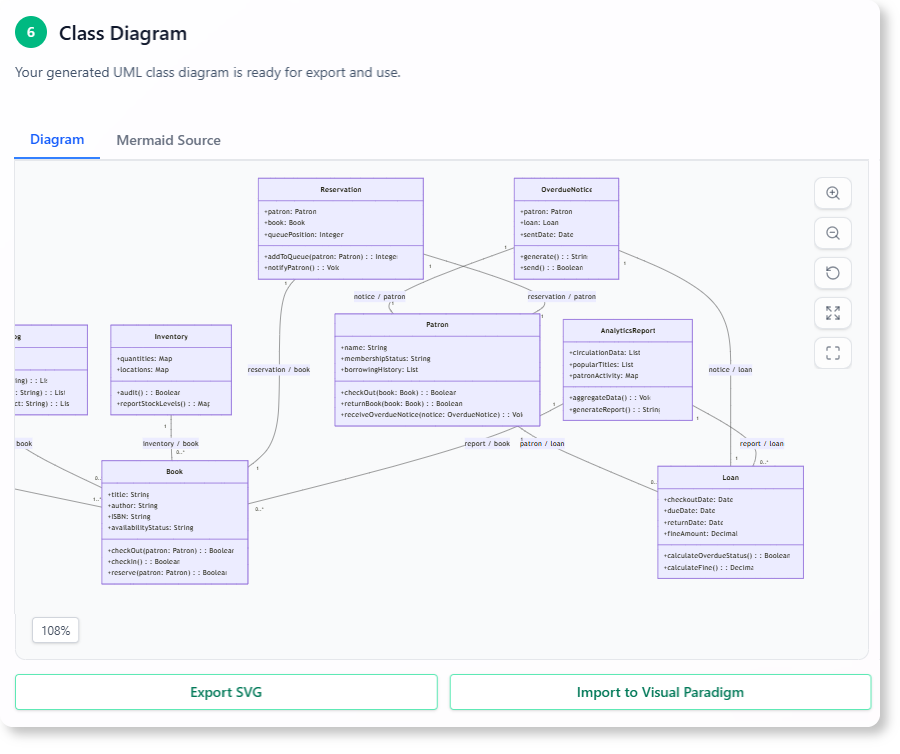
5. Benefits and Impact
A. For Students
- Learning Aid: Helps students understand OOD concepts by visualizing abstract ideas.
- Practice Tool: Enables hands-on practice with real-world examples.
B. For Developers
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerates the design phase by automating analysis.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes oversight in class and relationship identification.
- Collaboration: Provides a shared visual reference for teams.
C. For Educators
- Teaching Resource: Simplifies complex OOD concepts for classroom instruction.
- Assessment Tool: Allows students to submit diagrams for evaluation.
6. Availability and Access
A. Visual Paradigm Online
- Access: https://ai-toolbox.visual-paradigm.com/app/textual-analysis/
- Requirements: Combo Edition (or higher) subscription.
B. Visual Paradigm Desktop
- Access: Tools > App > Textual Analysis Tool.
- Requirements: Professional Edition (or higher) with active software maintenance.
7. Summary
A. Key Takeaways
- The AI Textual Analysis Tool automates the transformation of natural language into UML Class Diagrams.
- It follows a to ensure thorough and accurate analysis.
- The tool is valuable for students, developers, and educators, reducing manual effort and improving design accuracy.
B. Future Potential
- Integration with other design tools.
- Expansion to support additional UML diagrams (e.g., Sequence, Use Case).
- Enhanced AI capabilities for more complex problem domains.
8. Conclusion
The AI Textual Analysis Tool by Visual Paradigm represents a significant leap in software design automation. By leveraging AI to bridge the gap between textual descriptions and structured UML diagrams, it empowers users to create precise, efficient, and scalable software architectures with ease.
Would you like to explore a specific aspect of this tool further, such as its or ?