1. Introduction
The C4 Model is a widely adopted standard for visualizing software architecture. It breaks down complex systems into four hierarchical levels: Context, Container, Component, and Code. While generic AI chatbots (like public models) can generate C4-like diagrams from text prompts, Visual Paradigm (VP) offers specialized tools—such as the AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator, AI Diagramming Chatbot, and C4 PlantUML Studio—that provide structured, consistent, and professional-grade documentation.
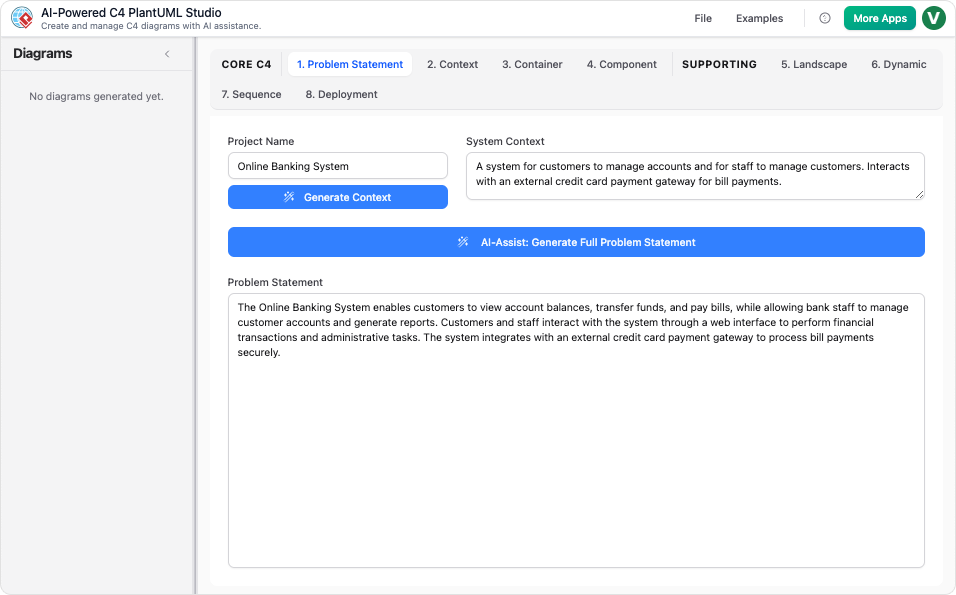
This review explores the advantages, limitations, and use cases for both approaches, helping you determine which tool aligns with your project’s needs.
2. Feature Comparison: Generic AI Chatbot vs. Visual Paradigm
A. Architectural Enforcement
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- Generates diagrams based on probabilistic text interpretation.
- No built-in C4 compliance: May produce inconsistent notation or incorrect hierarchical relationships.
- Example: If you ask for a Container Diagram, the chatbot might generate shapes and labels but won’t enforce C4 standards (e.g., proper use of containers, components, or relationships).
-
Visual Paradigm:
- Strict C4 compliance: Automatically applies correct notation, labels, and relationships.
- Example: If you describe a system, VP ensures that Containers are properly nested under the System Context and Components are accurately placed within Containers.
B. Hierarchical Consistency
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- Diagrams are generated independently, leading to inconsistencies between levels.
- Example: A Context Diagram might not align with a Container Diagram if generated separately.
-
Visual Paradigm:
- Structured workflow: Ensures that changes in one diagram (e.g., adding a Container) automatically update related diagrams.
- Example: If you modify a Container, VP updates all dependent Component Diagrams to reflect the change.
C. Output Format & Portability
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- Outputs static images or raw text, which are difficult to edit or version control.
- Example: A PNG diagram cannot be easily modified or integrated into a CI pipeline.
-
Visual Paradigm:
- Generates PlantUML code, which is:
- Version-controllable (e.g., via Git).
- Integratable into CI/CD pipelines.
- Editable for fine-tuning.
- Example: You can export PlantUML code, modify it, and regenerate diagrams without starting from scratch.
- Generates PlantUML code, which is:
D. Scope Coverage
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- Typically limited to basic Context or Container diagrams.
- Example: Struggles to generate Deployment or Dynamic Diagrams without manual intervention.
-
Visual Paradigm:
- Full C4 suite generation: Instantly creates all six C4 views:
- Context
- Container
- Component
- Landscape
- Dynamic
- Deployment
- Example: With a single prompt, VP can generate a complete set of diagrams for a microservices architecture.
- Full C4 suite generation: Instantly creates all six C4 views:
E. Workflow Support
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- Requires manual input for all content.
- Example: You must describe every element (e.g., “Add a Redis Container”) and regenerate the diagram.
-
Visual Paradigm:
- AI-assisted drafting: Uses conversational commands to:
- Add/remove components.
- Restructure responsibilities.
- Update relationships.
- Example: You can say, “Add a Kafka Container for event streaming,” and VP updates all related diagrams.
- AI-assisted drafting: Uses conversational commands to:
F. Cost
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- Often free or low-cost (e.g., public AI models).
-
Visual Paradigm:
- Requires a subscription (Desktop or Online).
- Justified by professional-grade features and time savings.
4. Guidelines: When to Use Each Tool
Use a Generic AI Chatbot If:
- You need a quick, rough sketch of a system.
- You’re exploring ideas and don’t require strict C4 compliance.
- Your project is small-scale or non-critical.
Use Visual Paradigm If:
- You need professional, consistent C4 documentation.
- Your project requires version control and CI/CD integration.
- You want to accelerate documentation with AI-assisted drafting.
- You need (Context, Container, Component, Deployment, etc.).
4. Real-World Example
Scenario: Microservices Architecture Documentation
-
Generic AI Chatbot:
- You describe your system: “A microservice architecture with a React frontend, Node.js backend, and MongoDB database.”
- The chatbot generates a basic Context Diagram but struggles with:
- Container relationships (e.g., how services communicate).
- Component-level details (e.g., modules within the Node.js service).
- Output: A static image that requires manual updates.
-
Visual Paradigm:
-
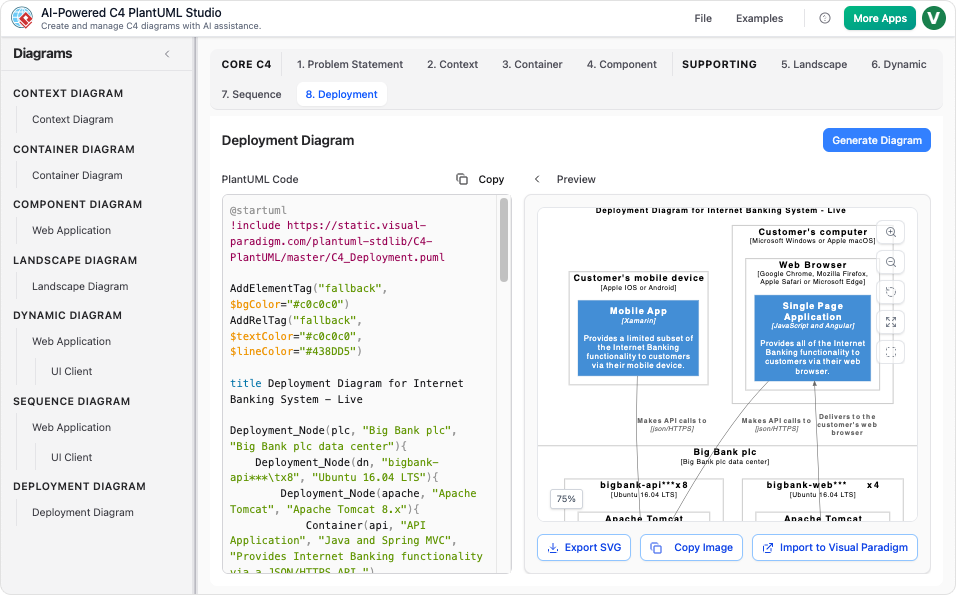 You input the same description.
You input the same description.- VP generates:
- A Context Diagram with external users and systems.
- A Container Diagram showing React, Node.js, and MongoDB.
- A Component Diagram detailing modules within Node.js.
- PlantUML code for version control.
- You can then:
- Edit diagrams via chat commands.
- Export to PlantUML for CI integration.
- Regenerate diagrams as the architecture evolves.
5. Conclusion
Key Takeaways:
- Generic AI Chatbots are useful for quick, informal visualizations but lack consistency, compliance, and scalability.
- Visual Paradigm’s C4 Tools provide structured, professional-grade documentation with , making them ideal for .
Final Recommendation:
- For hobby projects or brainstorming, a generic AI chatbot may suffice.
- For , Visual Paradigm is the clear choice due to its compliance, consistency, and integration capabilities.
- C4-PlantUML Studio | AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator (matches “AI-Powered C4 PlantUML Studio (C4-PlantUML Studio)” and “AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator”)
- AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator | Create Architecture Diagrams from Text (related AI tool entry point)
- C4 Component Diagram: A Definitive Guide to Your Code’s Internal Structure with AI (linked in multiple guide pages, e.g., from C4 System Context Guide)
- C4 Container Diagram: A Definitive Guide to Visualizing Your Software’s Building Blocks with AI (linked in multiple guide pages, e.g., from C4 System Context Guide)
- C4 Deployment Diagram (direct AI tool page for generating C4 Deployment Diagrams)
- C4 System Context Diagram: A Definitive Guide to Seeing the Big Picture with AI
- Generate the Complete C4 Model Instantly with Visual Paradigm’s AI Diagram Generator (featured in product updates, e.g., Visual Paradigm Desktop Updates)
- Streamline C4 Diagrams with Our New AI-Powered Markdown Editor (no exact matching page found; may be an older or internal feature reference)
- The Ultimate AI C4 Diagram Tool & Modeling Software
- New: Full C4 Model Support Added to Visual Paradigm Desktop (announced in AI Diagram Generator Release)
- C4 Diagram Tool & Modeling Software (core landing page for C4 tools)