This tutorial is based on the announcement of Visual Paradigm’s free AI Sequence Diagram Refinement Tool, launched on August 15, 2025. The tool leverages artificial intelligence to transform high-level user interaction descriptions into detailed, step-by-step sequences, making it easier to create accurate UML (Unified Modeling Language) sequence diagrams. Whether you’re a developer, system analyst, student, or anyone involved in system design, this tool simplifies the process of uncovering hidden complexities in interactions.
We’ll cover key concepts, step-by-step instructions with examples, and a summary to help you get started and master the tool.
Introduction to Sequence Diagrams and the Need for Refinement
Before diving into the tool, it’s essential to understand the basics. Sequence diagrams are a type of UML diagram that visualize how objects (or participants) in a system interact over time through a series of messages. They are commonly used in software engineering to model scenarios like user logins, data processing, or API integrations.
High-level descriptions of interactions (e.g., “user logs in”) often overlook underlying details, such as authentication checks or database queries. Manually expanding these can be time-consuming and error-prone. The AI Sequence Diagram Refinement Tool addresses this by automatically decomposing descriptions into comprehensive sequences, inferring implicit steps, and providing a blueprint for diagram creation.
Key Benefits Highlighted in the Tool’s Announcement
- Automation and Efficiency: Reduces manual effort, accelerating the design process.
- Completeness: Identifies overlooked steps to ensure robust designs.
- Accessibility: Free and integrated with Visual Paradigm’s platforms.
- User-Friendly: Suitable for beginners and experts alike.
Key Concepts
Here are the core concepts underpinning the tool and sequence diagram refinement:
- Interaction Decomposition:
- This refers to breaking down a high-level interaction into granular steps. For instance, a simple action like “user logs in” might decompose into: user enters credentials, system validates input, system queries database, system generates session token, etc.
- The AI uses natural language processing and domain knowledge to perform this intelligently.
- Participants (Actors and Objects):
- In sequence diagrams, participants include users, systems, databases, APIs, or other components. The tool identifies these automatically based on the description.
- Example: In a “checkout” process, participants might include Customer, Shopping Cart System, Payment Gateway, and Inventory Database.
- Messages and Sequences:
- Messages are the communications between participants, such as requests, responses, or asynchronous calls.
- The tool orders these chronologically, including synchronous (blocking) and asynchronous (non-blocking) interactions.
- Implicit messages (e.g., error handling or logging) are inferred to make the sequence complete.
- Implicit Steps:
- These are unspoken but necessary actions, like security checks or data validations, that humans might forget. The AI draws from best practices in system analysis to include them.
- UML Sequence Diagram Blueprint:
- The output isn’t a visual diagram but a textual breakdown that serves as a guide for creating one in tools like Visual Paradigm’s editor.
- Key elements include lifelines (vertical lines for participants), arrows for messages, and activation bars for processing time.
- Integration with Visual Paradigm:
- The tool is available via Visual Paradigm Online (web-based) or Desktop (application-based), ensuring seamless workflow from refinement to diagram building.
Understanding these concepts will help you interpret the AI’s output and refine it further if needed.
Accessing the Tool
The tool is free and accessible through Visual Paradigm’s platforms. No signup is required for basic use, but having a Visual Paradigm account enhances integration.
- For Online Users:
- Visit the direct link: https://ai-toolbox.visual-paradigm.com/app/sequence-diagram-refinement/.
- Log in if you have an account (optional for refinement but useful for saving diagrams).
- For Desktop Users:
- Open Visual Paradigm Desktop (ensure it’s the latest version, post-August 2025 release).
- Navigate to the menu: Tools > App.
- Select Sequence Diagram Refinement from the list.
Once accessed, the interface is straightforward: a text input for your description, a “Refine” button, and an output area for the decomposed sequence.
Step-by-Step Tutorial: How to Use the Tool
Follow these steps to refine an interaction and build a sequence diagram. We’ll use examples to illustrate.
Step 1: Describe the Interaction
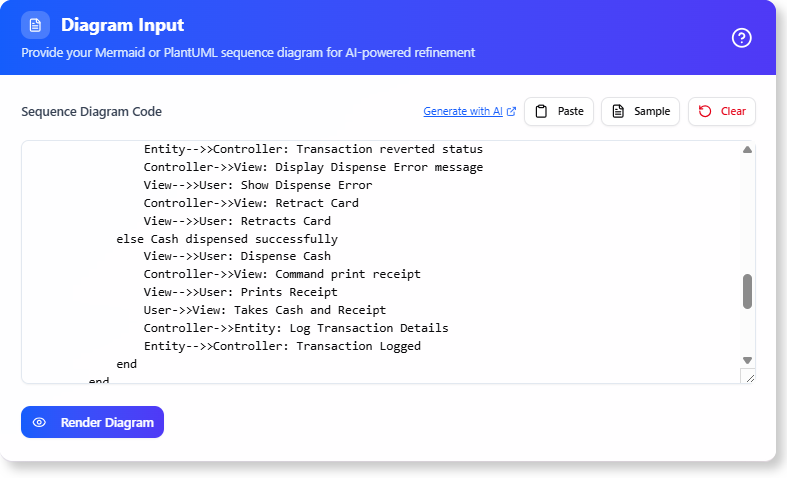
- Enter a concise, natural-language sentence describing the scenario.
- Tips:
- Be specific but high-level—avoid detailing steps yourself.
- Use action-oriented language (e.g., “User performs X”).
- Include context if relevant (e.g., “In an e-commerce app, customer checks out”).
Example 1: Simple Login Scenario
- Input: “User logs in to the system.”
- Why this? It’s a common interaction with hidden complexity.
Example 2: E-Commerce Checkout
- Input: “Customer checks out their shopping cart.”
- Why this? Involves multiple participants like payment systems and inventory.
Example 3: Password Reset
- Input: “User resets their password.”
- Why this? Demonstrates security-related implicit steps.
Step 2: Click “Refine”
- Submit your description. The AI processes it in seconds, analyzing the semantics to decompose it.
- Behind the scenes: The AI infers participants, messages, and order based on standard system behaviors.
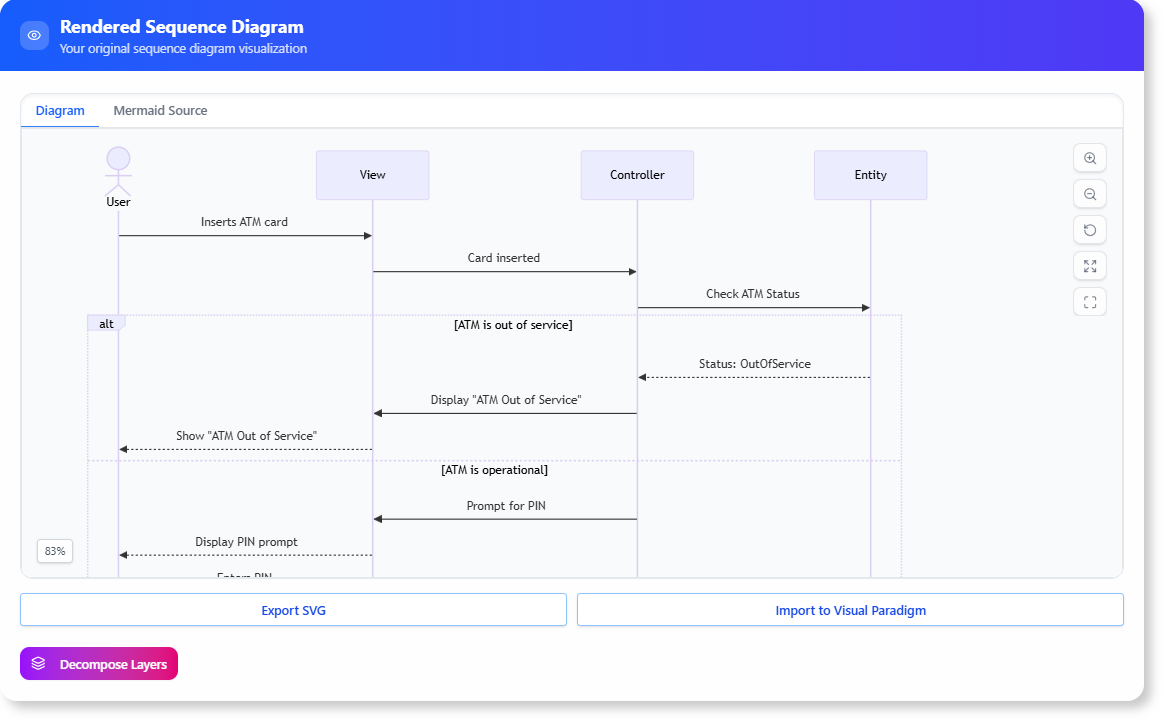
Step 3: Review the Decomposed Sequence
- The output is a textual list or structured breakdown, including:
- Participants (e.g., User, Authentication Server, Database).
- Sequential messages (e.g., 1. User sends credentials to Server; 2. Server queries Database).
- Implicit steps (e.g., “Validate input format” or “Handle errors”).
- Review for accuracy. You can edit the input and refine again if needed.
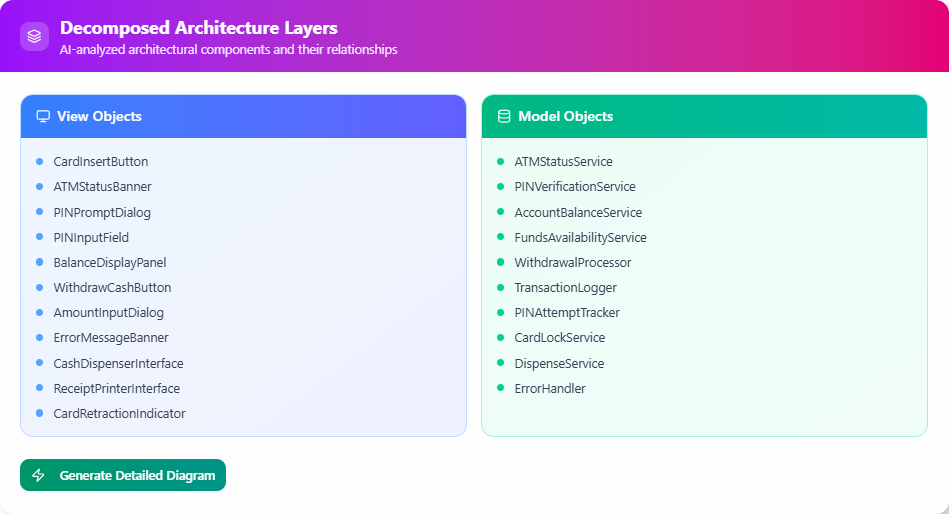
Example Output for “User logs in to the system” (Hypothetical based on tool description; actual output may vary):
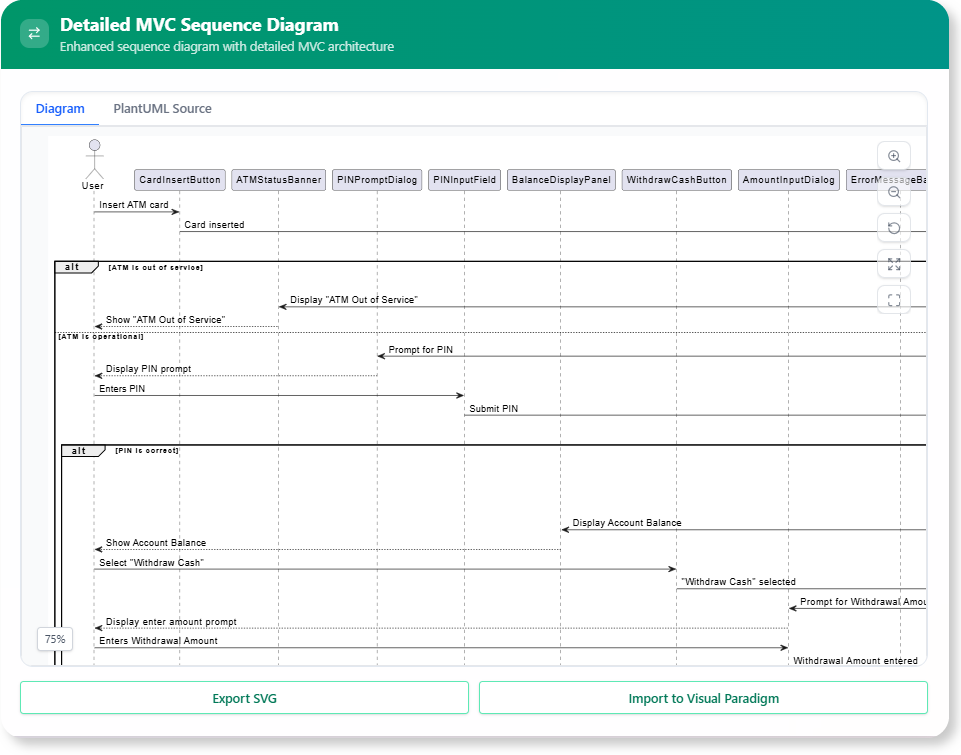
- Participants: User, Front-End Application, Authentication Server, User Database.
- Sequence:
- User enters username and password into Front-End Application.
- Front-End Application validates input format (implicit: check for empty fields).
- Front-End Application sends login request with credentials to Authentication Server.
- Authentication Server receives request and performs security check (implicit: rate limiting).
- Authentication Server queries User Database for credential verification.
- User Database responds with match status.
- If match, Authentication Server generates session token.
- Authentication Server sends success response with token to Front-End Application.
- Front-End Application stores token and redirects User to dashboard.
- (Error branch: If no match, send failure message.)
This reveals complexities like validation and error handling that might be missed manually.
Example Output for “Customer checks out their shopping cart”:
- Participants: Customer, E-Commerce Website, Shopping Cart System, Payment Gateway, Inventory Database, Email Service.
- Sequence:
- Customer reviews cart and clicks “Checkout” on E-Commerce Website.
- E-Commerce Website retrieves cart details from Shopping Cart System.
- Shopping Cart System calculates total (implicit: apply discounts/taxes).
- E-Commerce Website prompts Customer for payment info.
- Customer submits payment details.
- E-Commerce Website sends payment request to Payment Gateway.
- Payment Gateway processes transaction and responds with approval/denial.
- If approved, E-Commerce Website updates Inventory Database (implicit: reduce stock).
- Inventory Database confirms update.
- E-Commerce Website notifies Email Service to send confirmation.
- Email Service sends email to Customer.
- (Error branch: If payment fails, notify Customer and rollback changes.)
This example highlights multi-system integrations.
Step 4: Build Your Diagram
- Copy the decomposed sequence into Visual Paradigm’s UML editor.
- Create lifelines for each participant.
- Draw message arrows in order.
- Add notes for implicit steps or branches (e.g., alt fragments for conditions).
- Export or save the diagram for your project.
Tips for Diagram Creation:
- Use tools like auto-layout in Visual Paradigm to organize.
- Test the sequence logically: Does it handle edge cases?
- Iterate: Refine the description if the output misses domain-specific details.
Advanced Tips and Best Practices
- Handling Complex Scenarios: For intricate systems, break descriptions into sub-interactions (e.g., refine “login” separately from “checkout”).
- Customization: If the AI misses something, add hints in your description (e.g., “User logs in using OAuth”).
- Integration with Other Tools: Export refined sequences to code generators or documentation tools.
- Limitations: The tool is AI-based, so outputs are probabilistic—always verify for critical projects.
- Free Usage: No limits mentioned, but heavy use might require a premium account for advanced features.
Summary
The AI Sequence Diagram Refinement Tool from Visual Paradigm revolutionizes system design by automating the decomposition of high-level interactions into detailed sequences, ensuring completeness and accuracy in UML sequence diagrams. Key concepts include interaction decomposition, participant identification, message sequencing, and implicit step inference. Accessing it is easy via online or desktop platforms, and the workflow—describe, refine, review, build—is intuitive.
Through examples like login, checkout, and password reset, we’ve seen how the tool uncovers hidden steps, saving time and reducing errors. This free tool empowers users to create professional-grade designs efficiently. To get started, visit the link provided or explore Visual Paradigm’s resources. For more details, check the official announcement at https://updates.visual-paradigm.com/releases/free-ai-sequence-diagram-refinement-tool/. Experiment with your own scenarios to see the full potential!