In software development, use cases are essential for capturing functional requirements, defining how users (actors) interact with a system, and ensuring that all scenarios are accounted for. Traditionally, creating use cases involves manual brainstorming, documentation, and diagramming, which can be time-intensive and prone to inconsistencies. Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Use Case Description Generator revolutionizes this by leveraging artificial intelligence to automate much of the process, making it faster, more structured, and collaborative.
This tutorial will guide you through:
- What the AI feature helps with: Key capabilities in automating use case development.
- Key concepts: Fundamental ideas behind use cases and how AI enhances them.
- Step-by-step examples: Practical walkthroughs using real-world scenarios.
- Why not use a free LLM?: Reasons to prefer Visual Paradigm’s integrated tool over generic free large language models (LLMs).
By the end, you’ll understand how this tool can streamline your workflow and produce professional outputs.
Section 1: What Visual Paradigm’s AI Feature Helps With in Automating Use Case Development
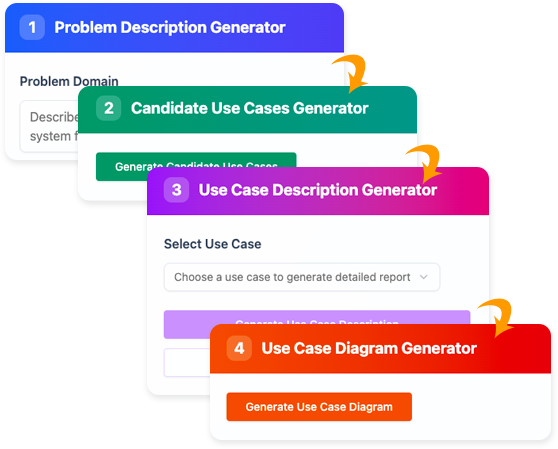
Visual Paradigm is a modeling and diagramming tool widely used for UML (Unified Modeling Language) designs, including use case diagrams. Its AI-Powered Use Case Description Generator is an app within the platform that uses AI to transform vague ideas into structured use case documentation. Here’s how it automates the process:
Core Automation Capabilities
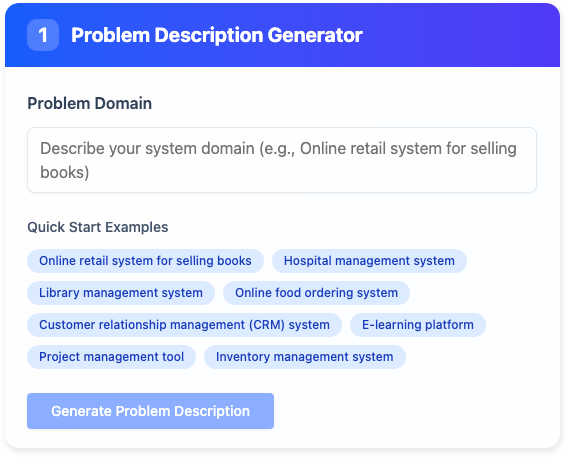
- Rapid Problem Description Generation: Starts with a simple prompt and generates a concise problem statement, setting the foundation without starting from scratch.
- Candidate Use Case Identification: Analyzes the problem to suggest a list of potential use cases, including names, descriptions, and associated actors. This reduces brainstorming time.
- Detailed Use Case Reporting: For each selected use case, it creates a comprehensive narrative, covering preconditions, postconditions, main flows, alternative flows, and exceptions.
- Visualization and Diagramming: Optionally generates editable Use Case Diagrams, which can be refined in Visual Paradigm Online for better stakeholder communication.
- Export and Collaboration Features: Outputs are exportable in Markdown or SVG formats, ensuring easy sharing and integration into project docs.
Benefits for the Development Process
- Efficiency: Cuts down manual writing and iteration time by 50-70% (based on typical user feedback in similar tools).
- Consistency: Ensures standardized terminology and structure across use cases, reducing errors in requirements gathering.
- Completeness: AI suggests overlooked elements like edge cases or additional actors, helping avoid gaps in analysis.
- Scalability: Ideal for large projects where manual use case creation could take weeks.
- Integration: Seamlessly ties into Visual Paradigm’s ecosystem for further modeling (e.g., transitioning to class diagrams or sequence diagrams).
This automation bridges the gap between high-level requirements and detailed analysis, making it invaluable for agile teams, business analysts, and developers.
Section 2: Key Concepts in Use Case Development and AI’s Role
Before diving into examples, let’s cover foundational concepts:
Key Use Case Concepts
- Use Case: A description of a system’s behavior from an external user’s perspective, focusing on “what” the system does (not “how”). It includes:
- Actors: Users or external systems interacting with your system (e.g., Customer, Admin).
- Preconditions: States required before the use case starts (e.g., User is logged in).
- Postconditions: Expected outcomes after successful execution.
- Main Flow: The happy path or primary sequence of steps.
- Alternative/Exception Flows: Variations or error handling paths.
- Use Case Diagram: A UML visual representation showing actors, use cases, and relationships (e.g., “extends” for optional behaviors, “includes” for reused steps).
- Problem Description: A narrative outlining the system’s purpose and challenges, serving as input for use case generation.
How AI Enhances These Concepts
AI in Visual Paradigm uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to:
- Parse prompts and infer relationships (e.g., identifying actors from context).
- Generate structured outputs based on best practices (e.g., following Alistair Cockburn’s use case template).
- Suggest improvements iteratively, ensuring alignment with industry standards like UML 2.0.
- Handle complexity by considering domain-specific knowledge (e.g., e-commerce vs. banking systems).
This makes use cases more than static docs—they become dynamic, editable artifacts for ongoing refinement.
Section 3: Step-by-Step Examples of Using the AI Feature
Let’s walk through two examples: a simple ATM system and a more complex e-commerce UI revamp. Assume you have Visual Paradigm installed or access to its online version.
Example 1: Basic ATM System
Scenario: You’re designing a basic ATM for banking.
- Launch the App:
- Open Visual Paradigm.
- Go to Tools > Apps.
- Search for “Use Case Description Generator” and click Start Now.
- Generate Problem Description:
- Enter prompt: “An ATM system for withdrawing cash and checking balances.”
- Click Generate Problem Description.
- AI Output (example): “The ATM system allows bank customers to perform financial transactions such as cash withdrawals, balance inquiries, and transfers without visiting a branch. It must ensure security through PIN authentication and handle errors like insufficient funds.”
- Generate Candidate Use Cases:
- Click Generate Candidate Use Cases.
| Use Case Name | Description | Actors |
|---|---|---|
| Withdraw Cash | User withdraws money from their account. | Customer |
| Check Balance | User views their account balance. | Customer |
| Transfer Funds | User transfers money to another account. | Customer |
| Authenticate User | Verifies user’s identity via PIN. | Customer, Bank System |
4. Generate Use Case Description:
- Select “Withdraw Cash”.
- Click Generate Use Case Description.
- AI Output (report excerpt in Markdown):
Use Case: Withdraw Cash
Actors: Customer
Preconditions: ATM is operational; Customer has a valid card and PIN.
Main Flow:
1. Customer inserts card.
2. System prompts for PIN.
3. Customer enters PIN.
4. System validates PIN.
5. Customer selects Withdraw.
6. Customer enters amount.
7. System checks balance and dispenses cash.
Postconditions: Cash dispensed; Account balance updated.
Exceptions: Invalid PIN (return to step 2); Insufficient funds (display error).
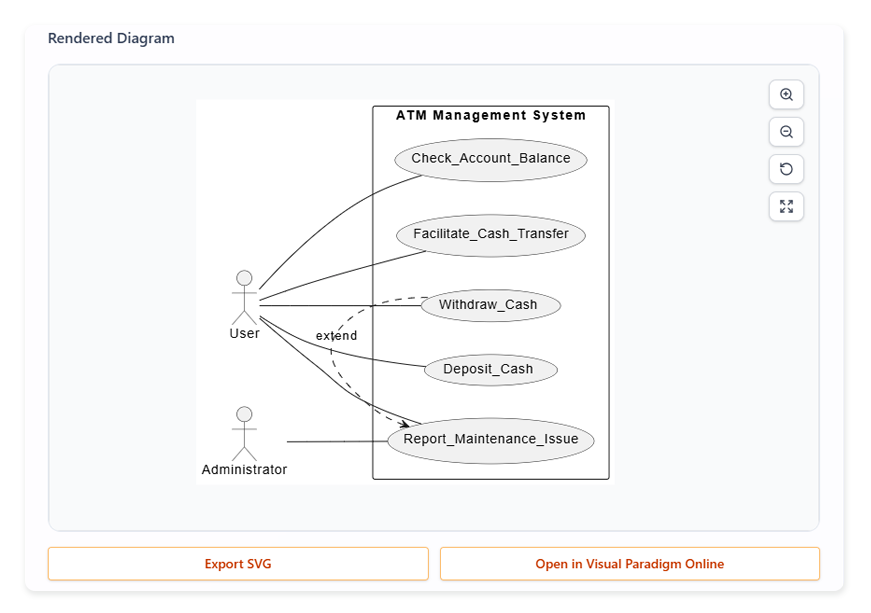
5. Visualize Use Case Diagram (Optional):
-
- Click Generate Use Case Diagram.
- View the diagram (actors as stick figures, use cases as ovals).
- Export as SVG or click Open in Visual Paradigm Online to edit (e.g., add “extends” for PIN recovery).
6. Export and Refine:
-
-
- Export the report as Markdown.
- Share with team for feedback.
-
This example automates from prompt to diagram in minutes.
Example 2: E-Commerce Shopping Cart UI Revamp
Scenario: Revamping a website’s shopping cart for better user experience.
- Generate Problem Description:
- Prompt: “I want to revamp the UI of our shopping cart website.”
- AI Output: “The current shopping cart website has outdated UI elements leading to high cart abandonment. The revamp aims to modernize the interface, improve navigation, and integrate features like one-click checkout for enhanced user satisfaction and conversion rates.”
- Generate Candidate Use Cases:
AI Output (table):Use Case Name Description Actors Add Item to Cart User adds products to their shopping cart. Shopper View Cart User reviews items in cart and totals. Shopper Checkout User proceeds to payment. Shopper, Payment Gateway Update Cart Quantity User changes item quantities. Shopper Apply Discount User enters promo codes. Shopper Generate Use Case Description:
- Select “Checkout”.
- AI Output: Detailed flow including guest vs. logged-in users, payment options, and error handling (e.g., failed payment).
- Generate and Edit Diagram:
- Create diagram showing relationships (e.g., “Checkout” includes “Apply Discount”).
- Edit in Visual Paradigm Online to add custom UI notes.
This demonstrates handling more abstract, UI-focused projects.
Section 4: Why Not Use a Free LLM to Do It?
Free LLMs like ChatGPT or Grok can generate text-based use cases from prompts, but they fall short compared to Visual Paradigm’s integrated AI for several reasons:
- Lack of Structure and Integration: Free LLMs produce unstructured text, requiring manual formatting into tables or diagrams. Visual Paradigm automates this with built-in templates, ensuring UML compliance, and directly integrates with diagramming tools for editable visuals—no copy-pasting needed.
- Inconsistency and Hallucinations: Generic LLMs may invent inaccurate details or miss domain-specific nuances (e.g., forgetting regulatory actors in banking). Visual Paradigm’s AI is fine-tuned for software modeling, drawing from best practices to ensure completeness and reliability.
- No Visual Outputs: Free LLMs can’t generate or edit diagrams natively. Visual Paradigm provides instant, editable Use Case Diagrams, crucial for visual learners and stakeholders.
- Collaboration and Export Limitations: LLMs output plain text; Visual Paradigm offers professional exports (Markdown, SVG) and seamless workspace integration for team editing, version control, and project linking.
- Efficiency in Iteration: With free LLMs, refining outputs means re-prompting from scratch. Visual Paradigm’s step-by-step interface allows guided edits, saving time on iterations.
- Cost vs. Value: While free, LLMs lack enterprise features like data privacy (important for proprietary projects) and support. Visual Paradigm’s AI is part of a paid ecosystem but justifies the cost through productivity gains—e.g., reducing analysis time from days to hours.
In summary, for professional, integrated automation, Visual Paradigm excels where free LLMs provide only basic text generation.
Getting Started and Best Practices
- Access: Download Visual Paradigm or use the online version at visual-paradigm.com.
- Tips: Start with clear, specific prompts. Review AI outputs for accuracy—AI assists, but human oversight ensures perfection. Use for agile sprints to quickly prototype requirements.
- Tutorial Resources: Check Visual Paradigm’s official docs or YouTube for video walkthroughs.
This tool empowers teams to focus on innovation rather than documentation drudgery. If you have a specific project, try it out!
| Tool | URL |
|---|---|
| Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot (Diagram Generation) | https://chat.visual-paradigm.com/ |
| AI Textual Analysis (Structured Design from Text) | https://www.visual-paradigm.com/features/ai-textual-analysis/ |
| AI Base Use Case Diagram Analyzer | https://www.visual-paradigm.com/features/ai-base-use-case-diagram-analyzer/ |
| AI-Powered UML & Software Design (Blog) | https://www.diagrams-ai.com/blog/uml-relevance-2025-ai-powered-modeling/ |











