What: Building a Library Book Borrowing System with AI-Powered Diagrams
Core Concept
The tutorial explains how to create a sequence diagram for a library book borrowing and returning system using AI-powered modeling tools like Visual Paradigm. A sequence diagram visually maps interactions between users, systems, and databases to show how processes like borrowing, returning, and fine checks work.
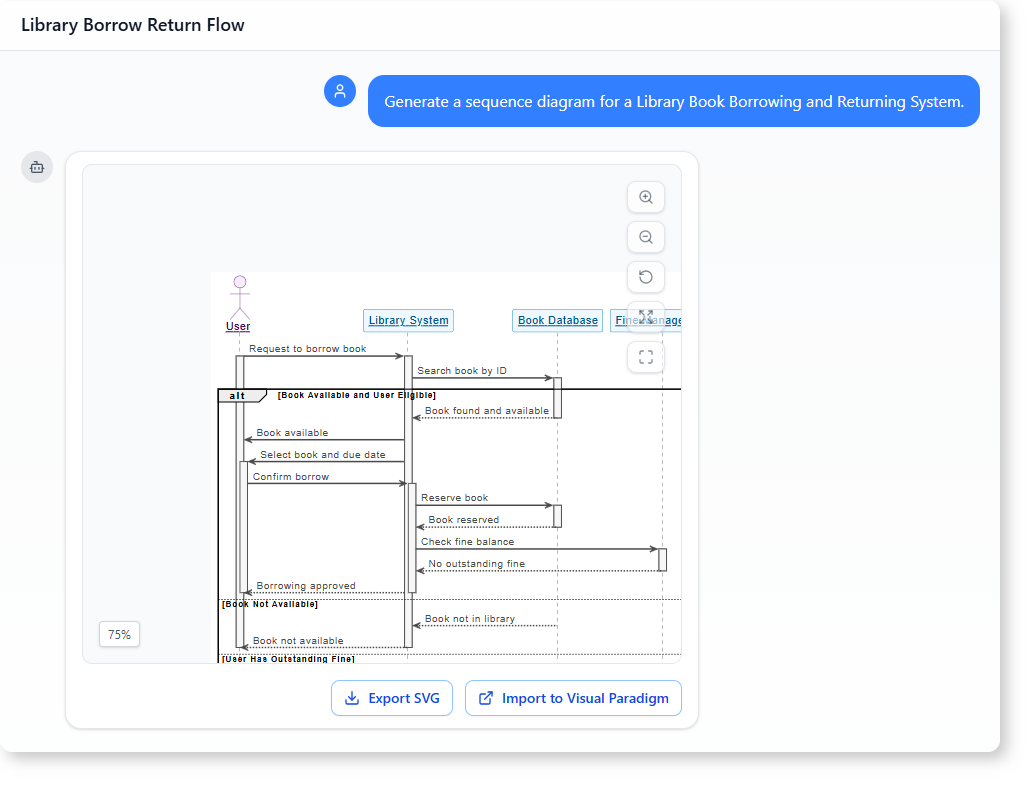
Key Components of the System
The AI-generated diagram includes:
- Participants:
- User (borrower)
- Library System (core logic)
- Book Database (availability checks)
- Fine Management (overdue penalties)
- Process Flows:
- Borrowing: User requests → System checks availability/fines → Approval/denial.
- Returning: User returns → System verifies → Updates records.
- Conditional Logic:
- Handles edge cases (e.g., “book unavailable,” “user has fines”).
Outputs
- A UML sequence diagram (visual representation).
- A structured report (text explanation for project submissions).
Why: Benefits of AI-Powered Modeling
1. Time Efficiency
- Traditional method: Manual diagramming (hours/days).
- AI method: Generate diagrams in minutes via text prompts.
2. Accuracy
- AI interprets natural language (e.g., “if the book is unavailable, show an error”) and converts it into correct UML syntax (e.g.,
alt/elseblocks). - Reduces human errors in logic or formatting.
3. Accessibility
- No prior UML knowledge needed: Ideal for students, beginners, or non-technical users.
- Report-ready outputs: AI generates explanations formatted for project submissions.
4. Scalability
- Works for any system (e.g., payment processes, inventory checks) by adjusting the prompt.
When: Ideal Use Cases
1. Academic Projects
- Example: Software design classes where students model real-world systems.
- Goal: Demonstrate understanding of system interactions without coding.
2. Professional Workflows
- Example: Teams designing workflows for libraries, banks, or e-commerce.
- Goal: Quickly prototype interactions before development.
3. Documentation
- Example: Creating visual aids for user manuals or training materials.
- Goal: Clarify complex processes for stakeholders.
Who: Stakeholders to Review the Diagram
1. Project Teams
- Developers: Validate logic before coding.
- Designers: Ensure user flows align with UI/UX.
2. Educators/Students
- Teachers: Assess accuracy of system logic in assignments.
- Students: Peer-review diagrams for clarity.
3. Librarians/End Users
- Librarians: Confirm real-world applicability (e.g., fine calculations).
- Borrowers: Provide feedback on user experience (e.g., error messages).
4. Technical Writers
- Use AI-generated reports to draft documentation.
How: Step-by-Step Tutorial
Step 1: Define the System Scope
- Prompt the AI with clear requirements:
“Generate a sequence diagram for a library book borrowing system. Include:
- User requests a book.
- System checks availability and fines.
- User returns the book.
- Handle cases: book unavailable, user has fines.”
Step 2: Generate the Diagram
- Open Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot.
- Paste your prompt.
- Review the AI-generated diagram (participants, flows, conditions).
Step 3: Refine the Output
- Edit manually if needed (e.g., add missing steps).
- Request explanations:
“Create a structured report explaining this diagram for a project.”
Step 4: Export and Share
- Diagram: Export as PNG/PDF.
- Report: Copy-paste the AI’s text explanation into your document.
Step 5: Validate with Stakeholders
- Share with librarians/developers to confirm logic.
- Adjust based on feedback (e.g., fine calculation rules).
Common Pitfalls and Fixes
| Pitfall | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overly complex prompts | Break into smaller steps (e.g., “borrowing” vs. “returning”). |
| Missing edge cases | Explicitly list conditions (e.g., “if user has fines”). |
| Diagram too cluttered | Simplify by splitting into sub-diagrams. |
Example Prompts for AI
- Basic:
“Generate a sequence diagram for borrowing a library book.”
- Detailed:
“Create a sequence diagram for a library system with:
- User, Library System, Book Database, Fine Management.
- Borrowing: check availability, fines, approve/deny.
- Returning: verify, update records, confirm success.”
- Report Generation:
“Explain this sequence diagram in a structured report format.”
Key Takeaways
- AI accelerates diagramming by converting text to UML.
- No expertise needed—just describe your system clearly.
- Validate with stakeholders to ensure real-world accuracy.
- Use for any system by adjusting the prompt.
Ready to try? Start with Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot and prompt:
“Generate a sequence diagram for a library book borrowing system with availability and fine checks.”











