1. What is Database Normalization?
Database normalization is a systematic approach to organizing data in a relational database to:
- Minimize redundancy (duplicate data)
- Improve data integrity (accuracy and consistency)
- Prevent anomalies (update, insert, and delete issues)
- Optimize storage and query performance
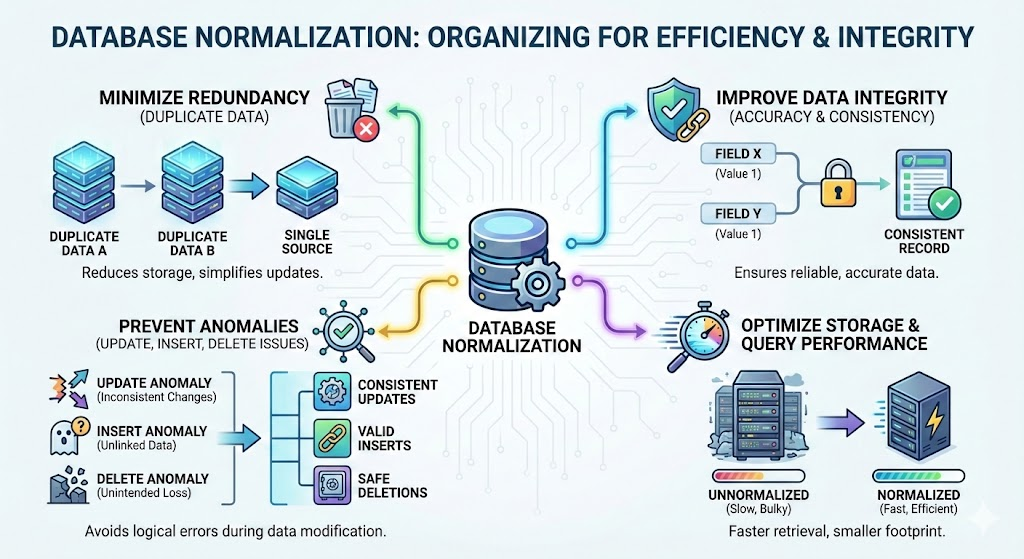
Normalization achieves this by decomposing tables into smaller, related tables and defining relationships between them using primary and foreign keys.
2. Why Normalize a Database?
Normalization addresses critical challenges in database design:
| Problem | Solution via Normalization |
|---|---|
| Data Redundancy | Eliminates duplicate data, reducing storage costs and inconsistencies. |
| Update Anomalies | Ensures changes to data (e.g., a customer’s address) are reflected in only one place. |
| Insert Anomalies | Prevents errors when adding new data (e.g., inserting a new order without a customer). |
| Delete Anomalies | Avoids unintended data loss (e.g., deleting an order shouldn’t delete the customer). |
| Query Efficiency | Smaller, well-structured tables speed up searches and reduce computational overhead. |
| Scalability | Simplifies future modifications (e.g., adding new fields or tables). |
3. When Should You Normalize?
Normalization is essential in the following scenarios:
When to Normalize
- High Data Redundancy: If your database stores the same information in multiple places (e.g., customer addresses in multiple tables).
- Frequent Updates: If data changes often (e.g., inventory systems, user profiles).
- Complex Relationships: If entities have multiple relationships (e.g., students, courses, and instructors).
- Data Integrity is Critical: If accuracy is non-negotiable (e.g., financial, healthcare, or legal systems).
- Long-Term Scalability: If the database is expected to grow or evolve over time.
When to Denormalize (or Stop at 3NF)
- Read-Heavy Applications: If your database is queried far more often than it’s updated (e.g., reporting systems, analytics dashboards).
- Performance Bottlenecks: If joins across normalized tables slow down queries (e.g., high-traffic e-commerce sites).
- Simple Use Cases: If the database is small and unlikely to grow (e.g., a personal contact list).
4. Who Should Use Database Normalization?
Normalization is relevant to anyone involved in database design, development, or management:
| Role | Why They Need Normalization |
|---|---|
| Database Administrators (DBAs) | Ensures efficient, reliable, and scalable database structures. |
| Software Developers | Designs databases that are easy to maintain, debug, and extend. |
| Data Architects | Creates robust data models that align with business requirements. |
| Students/Learners | Builds foundational knowledge for database design and relational theory. |
| Product Managers | Translates business needs into technical requirements for database schemas. |
| System Architects | Designs systems with optimal data storage and retrieval mechanisms. |
5. How to Normalize a Database: Step-by-Step with Examples
Normalization is achieved through a series of normal forms, each addressing specific types of redundancy and anomalies. Below is a practical guide to the first three normal forms (1NF, 2NF, 3NF), which are most commonly used.
First Normal Form (1NF)
Rule: Each table cell must contain a single, atomic value, and each column must have a unique name. No repeating groups or arrays.
Example: Unnormalized Table
| OrderID | Customer | Products |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Apples, Bananas |
| 2 | Alice | Grapes, Strawberries |
Problem: The Products column contains multiple values.
Solution: 1NF-Compliant Table
| OrderID | Customer | Product |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Apples |
| 1 | John | Bananas |
| 2 | Alice | Grapes |
| 2 | Alice | Strawberries |
Second Normal Form (2NF)
Rule: The table must be in 1NF, and all non-key attributes must depend on the entire primary key (no partial dependencies).
Example: 1NF Table (Not 2NF)
| StudentID | CourseID | CourseName | Instructor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | Math | Prof. Smith |
| 1 | 102 | Physics | Prof. Johnson |
| 2 | 101 | Math | Prof. Smith |
Problem: CourseName and Instructor depend only on CourseID, not the full primary key (StudentID + CourseID).
Solution: 2NF-Compliant Tables
Students Table:
| StudentID | StudentName |
|---|---|
| 1 | John |
| 2 | Alice |
| CourseID | CourseName | Instructor |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Math | Prof. Smith |
| 102 | Physics | Prof. Johnson |
Third Normal Form (3NF)
Rule: The table must be in 2NF, and no non-key attribute should depend on another non-key attribute (no transitive dependencies).
Example: 2NF Table (Not 3NF)
| EmployeeID | ProjectID | ProjectName | Manager |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | ProjectA | John |
| 1 | 102 | ProjectB | Alice |
| 2 | 101 | ProjectA | John |
Problem: Manager depends on ProjectID, not directly on the primary key (EmployeeID + ProjectID).
Solution: 3NF-Compliant Tables
Employees Table:
| EmployeeID | EmployeeName |
|---|---|
| 1 | John |
| 2 | Alice |
Projects Table:
| ProjectID | ProjectName |
|---|---|
| 101 | ProjectA |
| 102 | ProjectB |
EmployeeProjects Table:
| EmployeeID | ProjectID |
|---|---|
| 1 | 101 |
| 1 | 102 |
| 2 | 101 |
Higher Normal Forms (BCNF, 4NF, 5NF)
- Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF): Stricter than 3NF; eliminates all redundancy caused by functional dependencies.
- Fourth Normal Form (4NF): Handles multi-valued dependencies (e.g., a book with multiple authors).
- Fifth Normal Form (5NF): Deals with join dependencies (rarely used in practice).
6. How Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered DB Normalization Tool Streamlines the Process
Manual normalization can be time-consuming, error-prone, and complex, especially for large databases. Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered DB Normalization tool automates and simplifies the process, delivering production-ready schemas in minutes.
Key Features of Visual Paradigm’s AI Tool
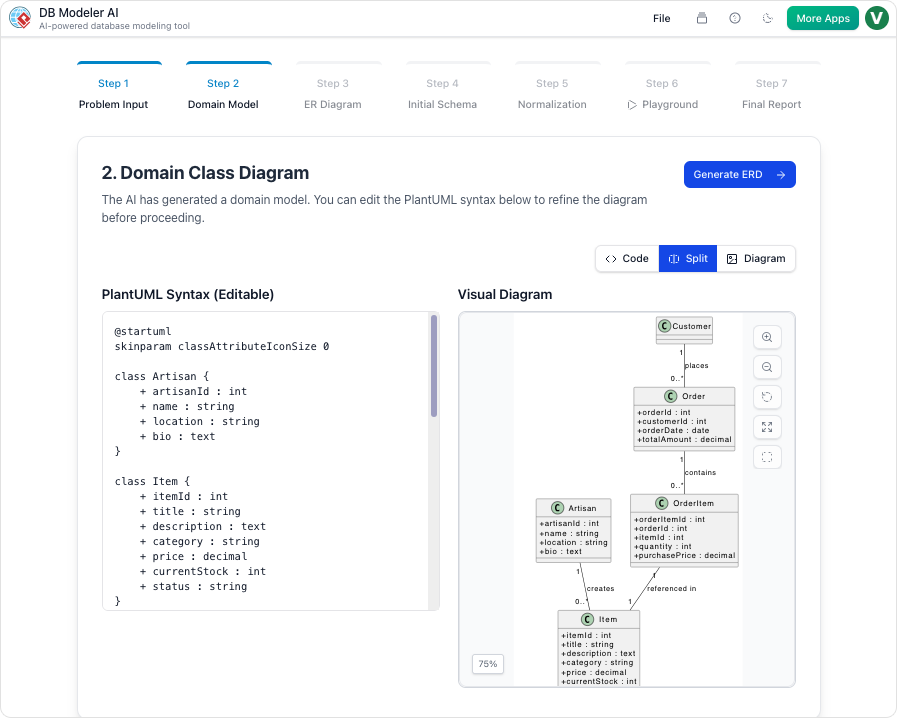
1. Automated Visual Diagrams
- What it does: Generates clear, professional ER (Entity-Relationship) diagrams from plain English descriptions.
- Why it matters: Visualizes relationships between tables, making it easier to spot redundancies and dependencies.
- Example: Describe “A library system with books, authors, and members,” and the tool generates a fully normalized schema with tables, keys, and relationships.
2. Step-by-Step Normalization Guidance
- What it does: Walks you through the normalization process from 1NF to 3NF (or higher) with explanations for each step.
- Why it matters: Helps beginners learn normalization while ensuring experts avoid mistakes.
- Example: The tool highlights partial dependencies in 2NF and suggests how to split tables to achieve 3NF.
3. Live In-Browser SQL Playground
- What it does: Lets you run real SQL queries on your normalized schema without installing software.
- Why it matters: Test your design instantly to ensure it meets performance and integrity requirements.
- Example: Write a query to join tables and verify that data is retrieved correctly.
4. AI-Assisted Workflow
- What it does: Uses AI to analyze your plain English description and generate a fully normalized database schema.
- Why it matters: Saves hours of manual work and reduces human error.
- Example: Input: “A hospital database with doctors, patients, and appointments.” Output: A 3NF-compliant schema with tables for
Doctors,Patients,Appointments, and relationships between them.
Who Should Use Visual Paradigm’s AI Tool?
| Role | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Developers | Rapidly designs and validates schemas for projects of any scale. |
| Students | Learns normalization concepts through interactive, hands-on tools. |
| Product Managers | Translates business requirements into technical data models without deep SQL knowledge. |
| System Architects | Prototypes complex data relationships quickly and visualizes system designs. |
7. Conclusion
Database normalization is a fundamental skill for designing efficient, scalable, and error-free databases. By following the 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF rules, you can eliminate redundancy, improve data integrity, and optimize performance. However, manual normalization can be complex and time-consuming.
Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered DB Normalization tool streamlines the process by:
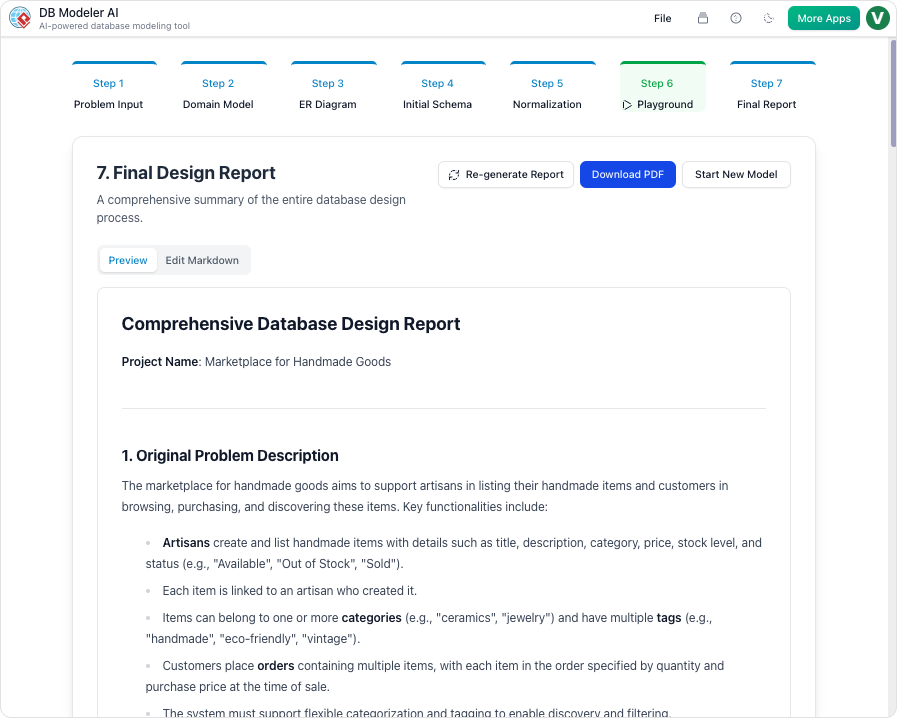
- Automating schema generation from plain English descriptions.
- Providing step-by-step guidance for normalization.
- Offering a live SQL playground to test designs.
- Generating visual ER diagrams for clarity.
Whether you’re a developer, student, or product manager, this tool helps you build production-ready databases faster and smarter.
Ready to Try It?
👉 Start Designing Your Database with Visual Paradigm AI Now
Have you used database normalization in a project? What challenges did you face? Let’s discuss!











