Introduction
The landscape of software architecture is undergoing a seismic shift. For decades, the foundation of any robust application—the database—was conceived through rigorous, manual labor. This process, known as the Evolution of Database Modeling, is now transitioning from the era of manual blueprints to a new age of AI-Driven Architecture.
Traditionally, designing data structures required deep expertise, isolated tools, and significant time investment. It was a high-friction process prone to human error, redundancy, and architectural debt. However, innovations such asVisual Paradigm’s DB Modeler AI have disrupted this status quo. By introducing an intelligent, guided 7-step workflow, this technology leverages generative AI to transform plain English descriptions into fully normalized, production-ready database schemas.
This comprehensive guide explores this evolution, highlighting the stark differences between legacy methods and modern AI capabilities. We will walk through the practical application of these tools using a classic online bookstore scenario, demonstrating how AI eliminates traditional pain points and accelerates professional database design.
The Traditional Struggle: Manual Constraints and High Friction
In the pre-AI era, database modeling was considered a labor-intensive craft reserved for specialists. The process was fraught with challenges that often slowed down development cycles and introduced vulnerabilities.
The Legacy Workflow
- The Blank Canvas: Designers would begin with empty workspaces in tools like ER/Studio, Lucidchart, or even physical pen-and-paper. There was no starting leverage; every entity had to be conceived from scratch.
- Manual Identification: The architect had to manually identify entities, attributes, relationships, primary keys (PKs), and foreign keys (FKs). This required a perfect mental model of the business logic before drawing a single line.
- The Normalization Headache: Moving from a rough draft to a deployed schema involves Normalization (1NF → 2NF → 3NF). This process looks for redundancies, partial dependencies, and transitive dependencies. Traditionally, this required painstaking manual analysis, which was highly prone to oversight and human error.
- Passive Tools: Legacy tools acted as digital drawing boards. They offered no intelligent suggestions, no automatic transitions between conceptual and logical models, and no validation beyond basic syntax checking.
- Testing Silos: Validation required setting up local database environments (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL), manually writing
INSERTscripts, and hoping that queries would reveal integrity issues.
The result of this manual approach was often significant architectural debt, long iteration cycles, and a steep learning curve that excluded non-experts like product managers or students from the design process.
The AI-Powered Paradigm Shift
DB Modeler AI, accessible viaVisual Paradigm’s online platform, represents a fundamental change in how we approach data. It acts not just as a tool, but as an “intelligent co-pilot.” utilizing Natural Language Processing (NLP) and extensive domain knowledge, it interprets business requirements to generate standards-compliant models.
Comparison: Traditional vs. AI-Driven Modeling
The following table outlines the key operational differences between the traditional manual approach and the modern AI-driven workflow.
| Feature | Traditional Manual Method | AI-Driven Method (DB Modeler AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Input Mechanism | Manual drag-and-drop; explicit definition of every column. | Natural Language (Plain English descriptions). |
| Speed | Days or weeks for complex schemas. | Minutes from concept to normalized schema. |
| Normalization | Manual analysis; prone to human error and oversight. | Automated, step-by-step guidance (1NF, 2NF, 3NF) with explanations. |
| Validation | Requires external DB setup and manual script writing. | Instant, in-browser SQL playground with AI-generated test data. |
| Accessibility | Requires deep SQL/Architecture knowledge. | Accessible to developers, PMs, students, and architects. |
| Output Quality | Dependent entirely on the user’s expertise. | Standardized, best-practice compliant, production-ready DDL. |
The 7-Step Guided Workflow
Visual Paradigm‘s DB Modeler AI utilizes a transparent, seven-step process that guides the user from a vague idea to a concrete, tested database schema.
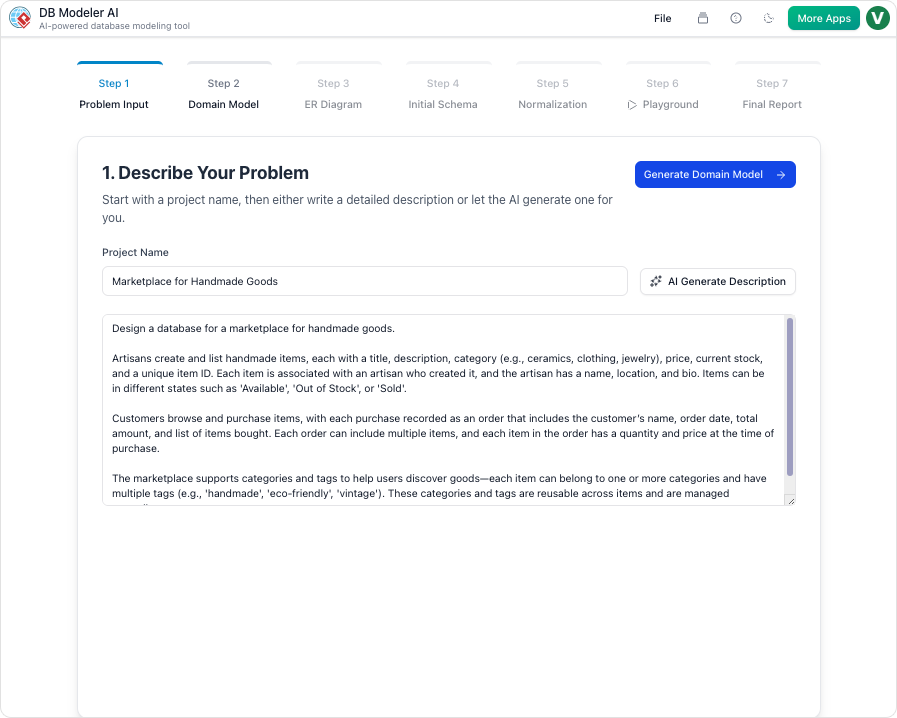
1. Problem Input
The process begins with a simple prompt. Users describe their application in plain English. For example: “Build a database for an online bookstore that manages books, authors, customers, orders, and allows tracking shipments.” The AI analyzes this text to extract core requirements.
2. Domain Class Diagram
Before diving into tables and keys, the AI generates a high-level conceptual view using PlantUML syntax. This helps visualizes the objects and their relationships in an abstract manner, ensuring the scope is correct before technical implementation.
3. ER Diagram Generation
The system automatically transitions from the conceptual model to a detailed logical Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD). It defines tables, columns, cardinalities, PKs, and FKs automatically.
4. Initial Schema Generation
The ERD is converted into SQL Data Definition Language (DDL). The tool typically defaults to widely used standards like PostgreSQL, ensuring compatibility with modern tech stacks.
5. Intelligent Normalization
This is arguably the most critical step. The AI progressively refines the schema to ensure data integrity:
- 1NF (First Normal Form): Ensures atomicity. It eliminates multi-value fields (e.g., ensuring a cell doesn’t contain a comma-separated list of authors).
- 2NF (Second Normal Form): Removes partial dependencies. It ensures that non-key attributes are dependent on the whole primary key, often splitting tables (e.g., separating Author details from the Book table).
- 3NF (Third Normal Form): Eliminates transitive dependencies. It ensures that columns are dependent only on the primary key, not on other non-key columns.
Crucially, the AI provides educational rationales for every decision, explaining why a table was split, making it a powerful learning tool.
6. Interactive Playground
Instead of requiring a local server, the tool offers a browser-based SQL environment. It automatically populates the schema with realistic, AI-generated sample data. This allows for immediate testing of queries and CRUD operations.
7. Final Report & Export
Once validated, the user can generate a Markdown design report, export the SQL scripts, and download diagrams in PDF or JSON formats. This serves as a “single source of truth” for the development team.
Practical Example: Designing an Online Bookstore
To demonstrate the power of this workflow, let us apply it to the online bookstore scenario mentioned in the source material.
Step 1: The Prompt
We input the following requirement: “I need a system for an online bookstore to manage books (with titles, authors, prices, categories, ISBN), customers (name, email, address), orders (date, status, total), and order items. Customers browse by author/category, place orders, and track shipments.”
Step 2 & 3: Visualizing the Structure
The AI instantly creates a Domain Class Diagram followed by an ER Diagram. It identifies that a Customer has a 1:N relationship with Orders, and that Books have a N:M (Many-to-Many) relationship with Orders, necessitating an intermediary OrderItem table.
Step 4 & 5: Refinement and Normalization
Initially, the schema might store the Author’s name directly inside the Books table. The AI identifies this as a violation of optimal database design.
- Action: The AI extracts
Authorinto its own table. - Result: The
Bookstable now contains anauthor_idforeign key. - Benefit: This eliminates redundancy; if an author changes their name, it only needs to be updated in one place.
Step 6: Testing in the Playground
With the schema generated, the AI seeds the database with realistic data (e.g., “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald). We can immediately run a test query to validate the structure:
SELECT b.title, a.name
FROM books b
JOIN authors a ON b.author_id = a.id
WHERE b.category = 'Fiction';If the query returns the expected results, the design is validated instantly.
Conclusion: Reducing Architectural Debt
The transition from manual blueprints to AI-driven architecture via tools likeVisual Paradigm DB Modeler AIdemocratizes high-quality database design. It bridges the gap between conceptual business requirements and technical implementation.
What once required weeks of expert labor and carried the risk of costly errors can now be accomplished in minutes. With built-in education, validation, and collaboration features, this technology empowers students, product managers, and developers to build faster, more reliable data architectures. As we move forward, integrating AI into the foundational stage of database modeling will likely become the standard for reducing architectural debt and accelerating innovation.











