1. What is BPMN?
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is the global standard for visualizing business processes. Developed and maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG), BPMN provides a consistent, intuitive, and executable way to model workflows across organizations.
BPMN uses graphical diagrams—known as Business Process Diagrams (BPDs)—to represent:
-
The sequence of activities,
-
Decision points,
-
Event triggers,
-
Interactions between participants,
-
Data flows, and
-
Process boundaries.
Its strength lies in its ability to bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technical teams, enabling clear communication across departments—from executives and analysts to developers and system architects.
✅ Key Facts:
-
Standard Version: BPMN 2.0.2 (released January 2014), adopted as ISO/IEC 19510:2013.
-
Execution Semantics: Unlike earlier notations, BPMN 2.0 introduced executable semantics, allowing diagrams to be directly deployed in process engines (e.g., Camunda, Activiti, Flowable).
-
Scope: Supports private processes (internal), public collaborations (multi-party), and choreographies (distributed interactions without central control).
📌 BPMN is not just a diagramming tool—it’s a complete modeling language for process design, analysis, automation, and optimization.
2. History of BPMN
BPMN evolved from a need to unify fragmented business modeling approaches into a single, standardized language.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2004 | First publication by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI). |
| 2005 | BPMI merges with the Object Management Group (OMG), setting the stage for formal standardization. |
| 2006 | OMG releases BPMN 1.0, introducing foundational notation. |
| 2010–2011 | Development of BPMN 2.0, launched in January 2011. Introduced execution semantics, improved structure, and support for complex processes. |
| 2014 | BPMN 2.0.2 released—final update to date, addressing minor issues and clarifying specifications. |
| 2013 | BPMN ratified as ISO/IEC 19510:2013, solidifying its status as an international standard. |
Since then, BPMN has become the de facto standard for business process modeling in enterprises worldwide.
3. Benefits of BPMN
BPMN delivers tangible value across organizations. Here’s why it’s widely adopted:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Standardization | OMG-maintained standard ensures consistency across teams, tools, and industries. |
| Universal Understandability | Intuitive symbols allow business users and IT professionals to collaborate effectively. |
| Improved Communication | Eliminates ambiguity between business requirements and technical implementation. |
| Process Analysis & Optimization | Enables simulation, bottleneck identification, and continuous improvement. |
| Support for Complex Workflows | Handles parallelism, conditional logic, exceptions, and event-driven behavior. |
| Interoperability & Automation | Diagrams can be exported to executable formats (e.g., BPEL, XML) and integrated with workflow engines. |
| Traceability & Compliance | Facilitates audit trails, regulatory compliance, and change management. |
💡 BPMN turns abstract ideas into actionable blueprints—making processes visible, measurable, and improvable.
4. The Goal of BPMN
The primary objective of BPMN is to establish a common visual language that all stakeholders can understand and use:
-
Business Analysts: Design, document, and refine processes.
-
Managers & Executives: Monitor KPIs, identify inefficiencies, and drive change.
-
Developers & IT Teams: Implement automation and integrate with enterprise systems.
-
End Users: Understand their roles and responsibilities within a process.
By aligning vision across levels, BPMN supports:
-
Process documentation
-
As-is vs. To-be analysis
-
Process reengineering
-
Digital transformation
-
End-to-end automation
5. Overview of BPMN
At its core, BPMN models business processes as sequences of flow elements governed by rules, events, decisions, and data.
🧩 Key Components of a BPMN Diagram:
-
Participants (Pools & Lanes): Define who performs what.
-
Flow Elements: Activities, events, gateways that define behavior.
-
Connecting Objects: Sequence flows, message flows, associations.
-
Data: Data objects, stores, inputs/outputs.
-
Artifacts: Annotations, groups for organization.
🔍 Process Types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Private Process | Internal workflow within a single organization (e.g., HR onboarding). |
| Public (Collaboration) Process | Involves multiple parties (e.g., customer and supplier). |
| Choreography | Describes interactions between participants without central control. |
BPMN diagrams can be simple (e.g., order fulfillment) or highly complex (e.g., multi-organization supply chains with parallel and event-driven paths).
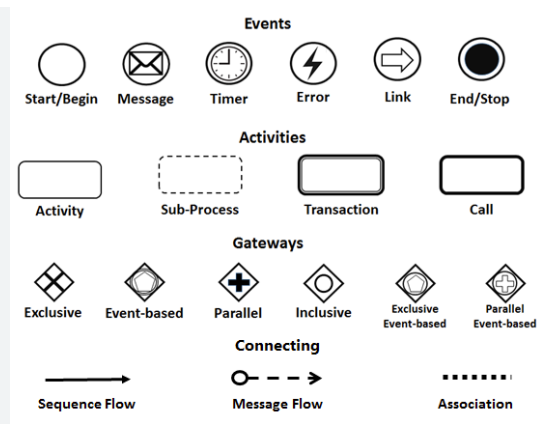
6. BPMN Notation: Core Elements Explained
BPMN elements are grouped into five categories:
1. Swimlanes (Participants)
Swimlanes visually separate responsibilities.
| Element | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pool | Represents a major participant (organization, department, role). | Customer, Logistics Department, Payment Gateway |
| Lane | Subdivision within a pool (e.g., team or function). | Customer Service, Warehouse, Finance |
✅ Use pools for external entities (e.g., partners, customers).
✅ Avoid over-nesting lanes—keep it simple and aligned with organizational structure.
2. Flow Elements (Core Behavior)
These define the dynamic aspects of a process.
🔹 Events (Circles)
Trigger or respond to something in the process.
| Type | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Start Event | ⚡ | Initiates the process (e.g., “Order Received”). |
| Intermediate Event | 🕒 | Occurs during the process (e.g., “Payment Received”, “Timer Expired”). |
| End Event | ✅ | Terminates the process (e.g., “Order Delivered”, “Error Handled”). |
Subtypes:
-
Message: External trigger (e.g., “Email Received”).
-
Timer: Time-based (e.g., “After 3 days”).
-
Error: Exception handling.
-
Conditional: Based on data (e.g., “If order > $100”).
🔹 Activities (Rounded Rectangles)
Actions performed in the process.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Task | Atomic unit of work. | “Verify Customer ID” |
| Sub-Process | A group of tasks that can be collapsed/expended. | “Process Payment” (can be expanded into child diagram) |
📌 Use sub-processes to manage complexity and enable drill-down analysis.
🔹 Gateways (Diamonds)
Control flow branching and merging.
| Type | Symbol | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Exclusive (XOR) | 🔒 | Only one path taken (e.g., “Is order valid?”). |
| Inclusive (OR) | 🔗 | One or more paths may execute. |
| Parallel (AND) | ✅ | All outgoing paths execute simultaneously. |
| Event-Based | 🌩️ | Waits for specific events (e.g., “Wait for Payment Confirmation”). |
⚠️ Use event-based gateways carefully—they introduce non-determinism.
3. Connecting Objects
Define how elements relate.
| Object | Symbol | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence Flow | Solid Arrow | Order of execution within a pool. |
| Message Flow | Dotted Arrow | Communication between pools (e.g., email, API call). |
| Association | Dotted Line | Links data or artifacts to flow elements (no execution order). |
🔄 Sequence Flow ≠ Message Flow:
Use sequence flow for internal logic.
Use message flow for inter-pool communication.
4. Data
Represents information used or produced.
| Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Data Object | A piece of data (e.g., “Order Form”, “Invoice”). |
| Data Input/Output | Shows data consumed or produced by an activity. |
| Data Store | Persistent storage (e.g., database, file system). |
📁 Data objects help track information flow and support data-driven decisions.
5. Artifacts
Non-execution elements for clarification.
| Artifact | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Group | Dotted box to group related elements (e.g., “Customer Onboarding Phase”). |
| Text Annotation | Notes or comments (e.g., “Requires approval from Manager”). |
📝 Use artifacts sparingly—avoid cluttering the diagram.
7. BPMN – A Practical Example
🛒 Online Distilled Water Ordering Process
Scenario:
A customer orders distilled water via phone or email. The company processes the order, assigns delivery, and fulfills it.
BPMN Diagram Structure:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Pools | Customer (external), Company (internal) |
| Lanes | Customer Service, Logistics, Finance (within Company pool) |
| Start Event | “Order Received via Phone or Email” |
| Gateway | Exclusive (XOR): “Channel = Phone?” → Yes → “Call Customer”; No → “Email Confirmation” |
| Activities | “Check Customer Status”, “Create Account (if new)”, “Process Payment”, “Assign Delivery” |
| Parallel Gateway | “Multiple Deliveries?” → Yes → Parallel delivery tasks |
| Message Flows | From Customer to Company (order), Company to Customer (confirmation) |
| End Events | “Order Fulfilled” or “Issue Resolved” |
📊 This diagram clarifies:
Who does what
When decisions happen
How information flows
Where delays might occur
(Visual: Imagine a clean flowchart with two pools, swimlanes, decision diamonds, and smooth sequence flows.)
8. Using Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tool
Visual Paradigm is a leading enterprise-grade modeling platform with full BPMN 2.0.2 compliance and powerful features for process design, simulation, and collaboration.
✅ Key Features of Visual Paradigm
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Intuitive BPMN 2.0 Modeler | Drag-and-drop interface; auto-routing of flows; real-time validation. |
| Business Process Diagram (BPD) | Professional-grade diagramming with templates and styles. |
| Process Drill-Down | Expand sub-processes into detailed child diagrams. |
| As-Is vs. To-Be Modeling | Compare current and future states with traceability. |
| Process Simulation & Animation | Run simulations to analyze performance, bottlenecks, and costs. |
| Resource & Cost Allocation | Assign people, time, and currency; generate cost/time charts. |
| RACI & CRUD Charts | Auto-generate RACI matrices (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) and CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) matrices. |
| Integration Capabilities | Import/export to XPDL, XML, Visio; integrate with UML, ERD, wireframes. |
| Working Procedure Editor | Define step-by-step instructions per task; generate full process specs. |
| Collaboration & Sharing | Team modeling, version control, cloud sync (VP Online), export to PDF/HTML. |
🎯 Ideal for both beginners and advanced users—perfect for process analysts, consultants, and enterprise architects.
🛠️ Step-by-Step: Creating a BPMN Diagram in Visual Paradigm
Step 1: Launch Visual Paradigm
-
Open Visual Paradigm Desktop or VP Online.
-
Sign in (free trial available).
Step 2: Create a New BPMN Diagram
-
Go to Diagram > New.
-
Select Business Process Diagram (BPD).
-
Name it: e.g.,
Order Fulfillment Process.
Step 3: Add Pools and Lanes
-
From the Toolbar, drag:
-
Pool→ “Customer” -
Pool→ “Company”
-
-
Inside “Company”, add lanes:
Customer Service,Logistics,Finance.
Step 4: Add Flow Elements
-
Drag:
-
Start Event → “Order Received”
-
Task → “Verify Order Details”
-
Exclusive Gateway → “Is Customer New?”
-
Task → “Create Customer Account”
-
Sub-Process → “Process Payment”
-
-
Use sequence flows to connect them logically.
Step 5: Add Interactions
-
Use message flow (dotted arrow) from
CustomertoCompanyfor order submission. -
Use message flow back for confirmation.
Step 6: Enhance with Data & Artifacts
-
Add data objects: “Order Form”, “Payment Receipt”
-
Add text annotations: “Requires 24h approval”
-
Use groups to group related tasks (e.g., “Payment Processing Phase”).
Step 7: Validate & Refine
-
Use Validation Tool (Ctrl+Shift+V) to check for BPMN compliance.
-
Fix errors: missing end events, invalid flow, incorrect gateway usage.
Step 8: Expand Sub-Processes
-
Double-click the “Process Payment” sub-process.
-
Open a new diagram to detail payment steps (e.g., validate card, charge, confirm).
Step 9: Simulate the Process
-
Go to Tools > Process Simulation.
-
Assign:
-
Resources (e.g., “Customer Service Agent”)
-
Time estimates (e.g., 5 min per task)
-
Costs (e.g., $1.50 per delivery)
-
-
Run simulation → View:
-
Completion time
-
Resource utilization
-
Queue times
-
Bottleneck analysis
-
Step 10: Export & Share
-
Export to:
-
PDF (for documentation)
-
HTML (for web sharing)
-
Image (PNG/SVG)
-
-
Generate:
-
RACI Matrix (from diagram)
-
Process Specification Document
-
-
Share via VP Online or team workspace.
✅ Pro Tip: Use “Compare As-Is & To-Be” feature to track improvements over time.
9. Best Practices for Effective BPMN Modeling
| Practice | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Start Simple | Begin with high-level views; add detail only when needed. |
| Use Swimlanes Wisely | Align with organizational structure—don’t overuse lanes. |
| Avoid Overlapping Flows | Keep diagrams clean and readable. |
| Name Elements Clearly | Use descriptive labels (e.g., “Approve Order” vs. “Task 1”). |
| Limit Gateways per Process | Too many decisions make diagrams hard to follow. |
| Use Sub-Processes for Complexity | Keep main diagram focused. |
| Validate Before Sharing | Ensure compliance with BPMN 2.0.2 standards. |
| Simulate Regularly | Uncover hidden inefficiencies and risks. |
🎯 Remember: A good BPMN diagram is not just correct—it’s clear, actionable, and valuable.
10. Related Resources & Further Learning
| Resource | Link | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Official OMG BPMN Specification (2.0.2) | https://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/ | Download full PDF of the standard. |
| BPMN.org | https://www.bpmn.org | Community hub with examples, tools, and tutorials. |
| Visual Paradigm BPMN Guide | https://www.visual-paradigm.com/guide/bpmn/what-is-bpmn/ | Beginner-friendly introduction. |
| Visual Paradigm Tutorials | https://www.visual-paradigm.com/tutorials/ | Step-by-step video and text guides. |
| Download Visual Paradigm | https://www.visual-paradigm.com/download/ | Free 30-day trial (desktop & cloud). |
📘 Recommended Learning Path:
Watch “Introduction to BPMN” (VP YouTube)
Complete “How to Draw BPMN Diagrams” tutorial
Try simulating a simple process
Explore RACI and CRUD generation
11. Conclusion
BPMN is more than a diagramming language—it’s a strategic enabler for process excellence. With BPMN 2.0.2 as the global standard, organizations can:
-
Document processes clearly,
-
Analyze performance,
-
Automate workflows,
-
Drive digital transformation.
Visual Paradigm empowers you to turn ideas into actionable models with:
-
Intuitive design,
-
Powerful simulation,
-
Seamless collaboration,
-
Full lifecycle support.
✅ Your Next Steps:
Download Visual Paradigm (free trial).
Create your first BPMN diagram (e.g., “Customer Onboarding”).
Simulate it. Identify bottlenecks.
Share insights with your team.
Start simple. Iterate often. Use BPMN to see, understand, improve, and automate your business processes.
📌 Final Thought:
“If you can’t describe a process clearly, you don’t understand it well enough to improve it.”
— BPMN is your tool to make the invisible, visible.
BPMN Articles
What is BPMN? – Visual Paradigm Guide: An introductory guide explaining the purpose, structure, and benefits of BPMN in business process design.
BPMN Notation Overview – Visual Paradigm Guide: A comprehensive overview of BPMN notation elements, including events, activities, gateways, and artifacts used in process modeling.
How to Draw a BPMN Diagram – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: A step-by-step tutorial on creating professional BPMN diagrams using an intuitive interface and industry best practices.
Understanding Pools and Lanes in BPMN – Visual Paradigm User Guide: A detailed explanation of how to use pools and lanes to represent different departments, organizations, or roles within a process.
As-Is to To-Be Business Process Modeling Tutorial: A guide on analyzing current business processes (As-Is) and designing improved future processes (To-Be) using BPMN tools.
How to Create a BPMN Conversation Diagram in Visual Paradigm: A comprehensive guide for modeling interactions between business partners using specialized conversation diagrams.
How to Generate a RACI Chart from BPMN Models: Instructions on how to automatically generate a RACI matrix from existing BPMN diagrams to clarify roles and responsibilities.
How to Animate Business Processes with Visual Paradigm: A tutorial on creating dynamic, animated business process diagrams to enhance visualization and team communication.
Unlocking Efficiency: Performing Gap Analysis with BPMN: An article explaining how BPMN can be leveraged to visualize and analyze shortfalls in business processes for optimization.
AI Business Process Improvement Tool – Visual Paradigm Product Updates: An announcement regarding a tool that uses AI to transition from a problem statement directly to diagrams, KPIs, and analysis.