This comprehensive guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is based on the provided sources. It outlines the purpose, core elements, and detailed behavior of the notation used to standardize business process modeling.
1. Overview of BPMN
BPMN is a graphical representation used to specify business processes within a model. It was originally developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) in 2000 and has been maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG) since 2004.
The primary objective of BPMN is to provide a notation that is intuitive for business users while remaining powerful enough to represent complex process semantics for technical users. While the basic shapes are similar to standard flow diagrams, BPMN allows modelers to represent specific business actions, such as messaging departments or escalating issues.
2. Core BPMN Elements
The sources identify four primary elements used to construct a process model:
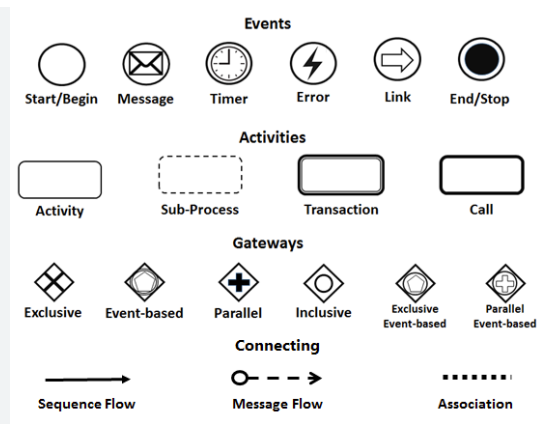
-
Activities: Represent the actual work performed within a business process.
-
Gateways: Used to control the divergence and convergence of sequence flows, effectively acting as decision points or merge points.
-
Flows:
-
Sequence Flow: Shows the specific order in which activities are performed.
-
Message Flow: Shows the communication or flow of messages between two different participants.
-
-
Events: Represent something that “happens” during a process, rather than a task being performed.
3. Detailed Guide to Events
Events are a critical component of BPMN and are visually represented as circles. They are categorized by where they occur in the process and how they behave.
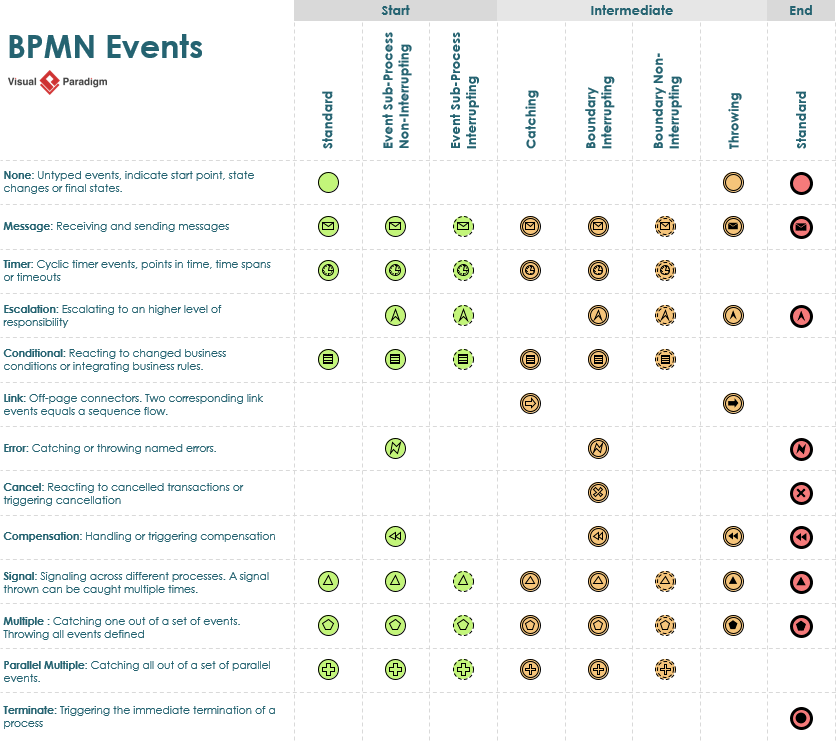
Classification by Position
-
Start Events: Indicated by a thin narrow line, these signify where a process begins. Every process must start with an event.
-
Intermediate Events: Indicated by a thin double line, these occur between the start and end of a process.
-
End Events: Indicated by a thick single line (or a filled outer circle), these signify the conclusion of a process. Every process has at least one end event.
Event Behaviors and Markers
BPMN 2.0 supports over 60 different types of events, often identified by Internal Markers (icons inside the circle).
-
Catching vs. Throwing:
-
Catching events have a defined trigger and start once that trigger is “fired”; they are visually identified by unfilled internal markers.
-
Throwing events are triggered by the process itself to create a notification; they are identified by filled internal markers.
-
-
Boundary Events: These are intermediate events attached to the boundary of an activity. They can be triggered at any time while that specific activity is being performed.
-
Interrupting vs. Non-Interrupting:
-
Interrupting Events: Represented by a solid line. When triggered, the current task stops immediately, and the flow moves to a new path.
-
Non-Interrupting Events: Represented by a dashed line. When triggered, the original task continues to completion while a parallel flow begins from the event.
-
Summary Table of Visual Indicators
| Feature | Visual Style | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Start Event | Thin single circle | The process begins here. |
| Intermediate Event | Double circle | Happens during the process. |
| End Event | Thick/Filled outer circle | The process ends here. |
| Interrupting | Solid line | Stops the current activity immediately. |
| Non-Interrupting | Dashed line | Allows the activity to finish while starting a new path. |
| Catching | Unfilled marker | Waiting to receive a signal/trigger. |
| Throwing | Filled marker | Generating a signal/trigger. |
BPMN Articles
-
What is BPMN? – Visual Paradigm Guide: An introductory guide explaining the purpose, structure, and benefits of BPMN in business process design.
-
BPMN Notation Overview – Visual Paradigm Guide: A comprehensive overview of BPMN notation elements, including events, activities, gateways, and artifacts used in process modeling.
-
How to Draw a BPMN Diagram – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: A step-by-step tutorial on creating professional BPMN diagrams using an intuitive interface and industry best practices.
-
Understanding Pools and Lanes in BPMN – Visual Paradigm User Guide: A detailed explanation of how to use pools and lanes to represent different departments, organizations, or roles within a process.
-
As-Is to To-Be Business Process Modeling Tutorial: A guide on analyzing current business processes (As-Is) and designing improved future processes (To-Be) using BPMN tools.
-
How to Create a BPMN Conversation Diagram in Visual Paradigm: A comprehensive guide for modeling interactions between business partners using specialized conversation diagrams.
-
How to Generate a RACI Chart from BPMN Models: Instructions on how to automatically generate a RACI matrix from existing BPMN diagrams to clarify roles and responsibilities.
-
How to Animate Business Processes with Visual Paradigm: A tutorial on creating dynamic, animated business process diagrams to enhance visualization and team communication.
-
Unlocking Efficiency: Performing Gap Analysis with BPMN: An article explaining how BPMN can be leveraged to visualize and analyze shortfalls in business processes for optimization.
-
AI Business Process Improvement Tool – Visual Paradigm Product Updates: An announcement regarding a tool that uses AI to transition from a problem statement directly to diagrams, KPIs, and analysis.